Finally a brain test showed which medications would help. - The NeuroDevelopment Center
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Trial and error medication: Even in the hands of the very best psychiatrists, prescribing medication is a trial and error process. The doctor evaluates patterns of symptoms, makes a diagnosis, then prescribes a medication that research has shown, on average, to be helpful to those with that diagnosis. But there’s a rub: For most disorders, there are multiple medications that have been found effective. And no medication has been found to be effective for all individuals with that disorder. Individuals […]

Addressing Outcome Measure Variability in Myasthenia Gravis Clinical Trials

Clinical Characteristics of Seizures and Epilepsy in Individuals With Recurrent Deletions and Duplications in the 16p11.2 Region

Grey matter connectome abnormalities and age-related effects in antipsychotic-naive schizophrenia - eBioMedicine

Genetic architecture of the white matter connectome of the human brain

The Gut Microbiome and the Brain Hopkins Bloomberg Public Health Magazine

Predicting 2-year neurodevelopmental outcomes in extremely preterm infants using graphical network and machine learning approaches - eClinicalMedicine

Hemispheric asymmetry in cortical thinning reflects intrinsic organization of the neurotransmitter systems and homotopic functional connectivity

Insights and opportunities for deep brain stimulation as a brain circuit intervention: Trends in Neurosciences

Neurodevelopmental genes: Solving cold cases - Boston Children's Answers
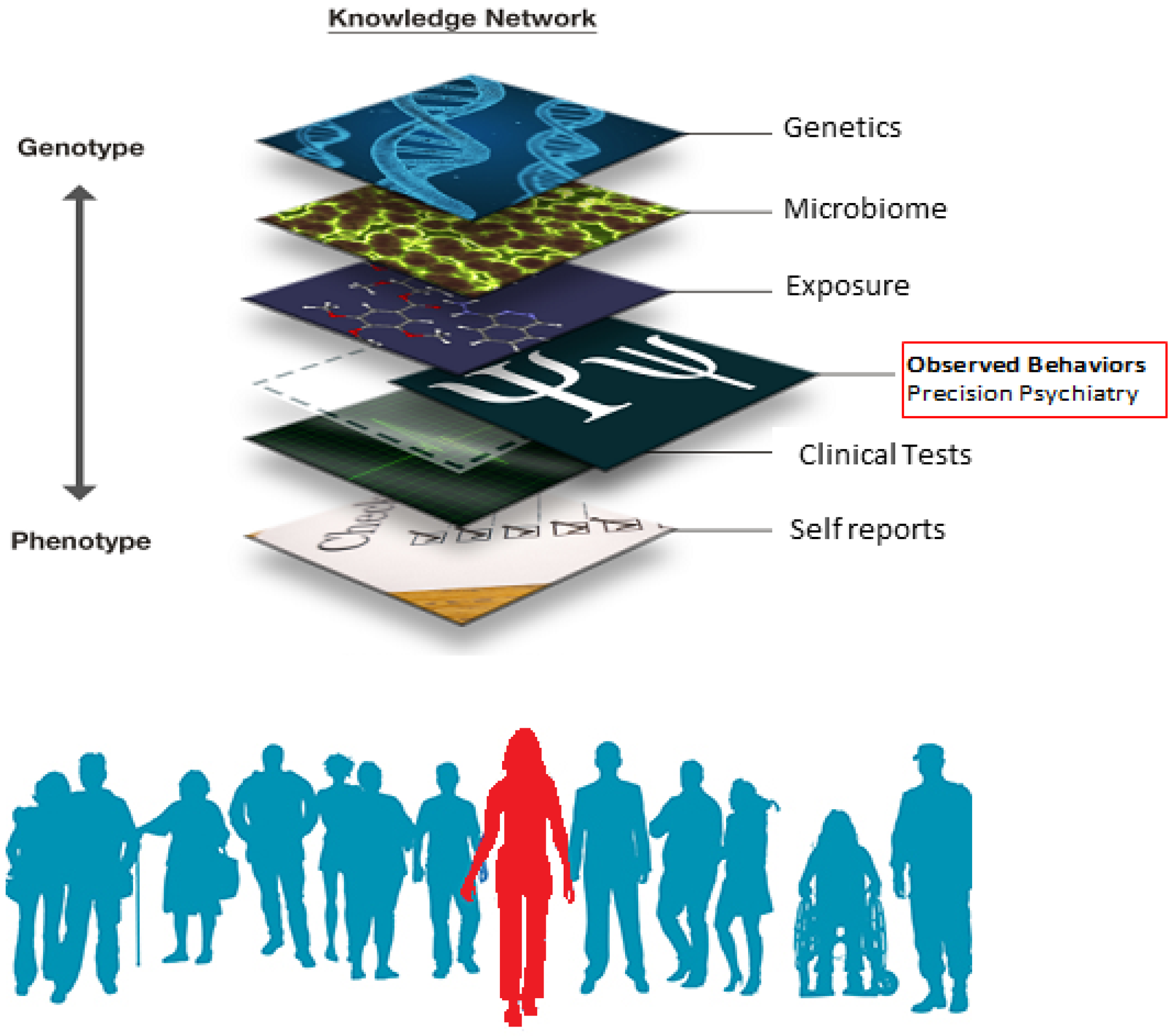
JPM, Free Full-Text

Years of Prozac Alter Lipids in Young Monkeys' Brains: Study
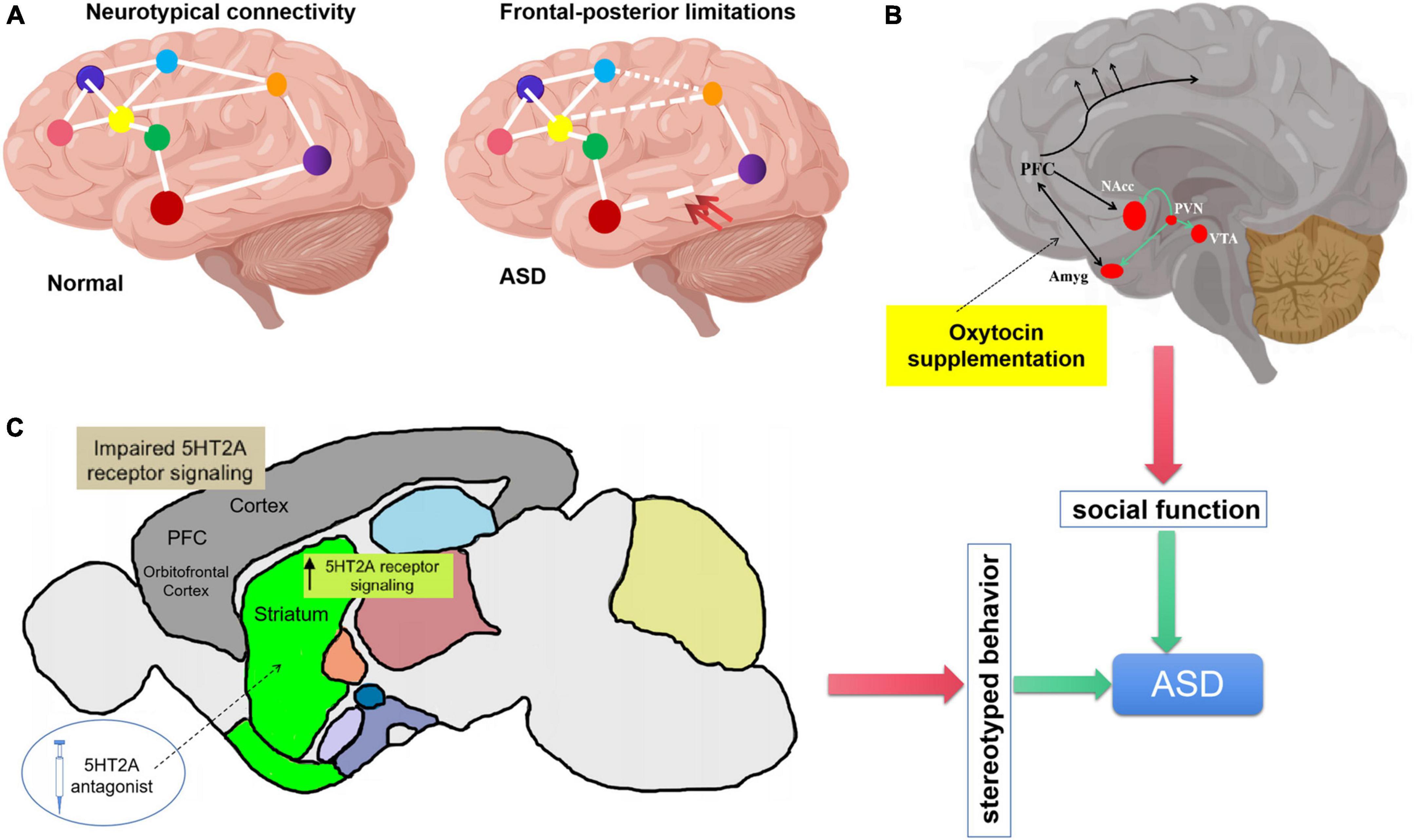
Frontiers Oxytocin and serotonin in the modulation of neural function: Neurobiological underpinnings of autism-related behavior

Neurodevelopmental disorders - The Lancet Psychiatry

Human brain cells transplanted into rat brains hold promise for neuropsychiatric research, News Center
Predicting Which Glioblastoma Patients Will Respond to Immunotherapy







