Are teicoplanin-non-susceptible Staphylococcus epidermidis strains increasing?
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Researchers elucidated the incidence patterns of teicoplanin-non-susceptible Staphylococcus epidermidis (Teico-NS S. epidermidis) over six years.

Figure. Time-kill kinetic challenge of (a) S. aureus, (b) S.
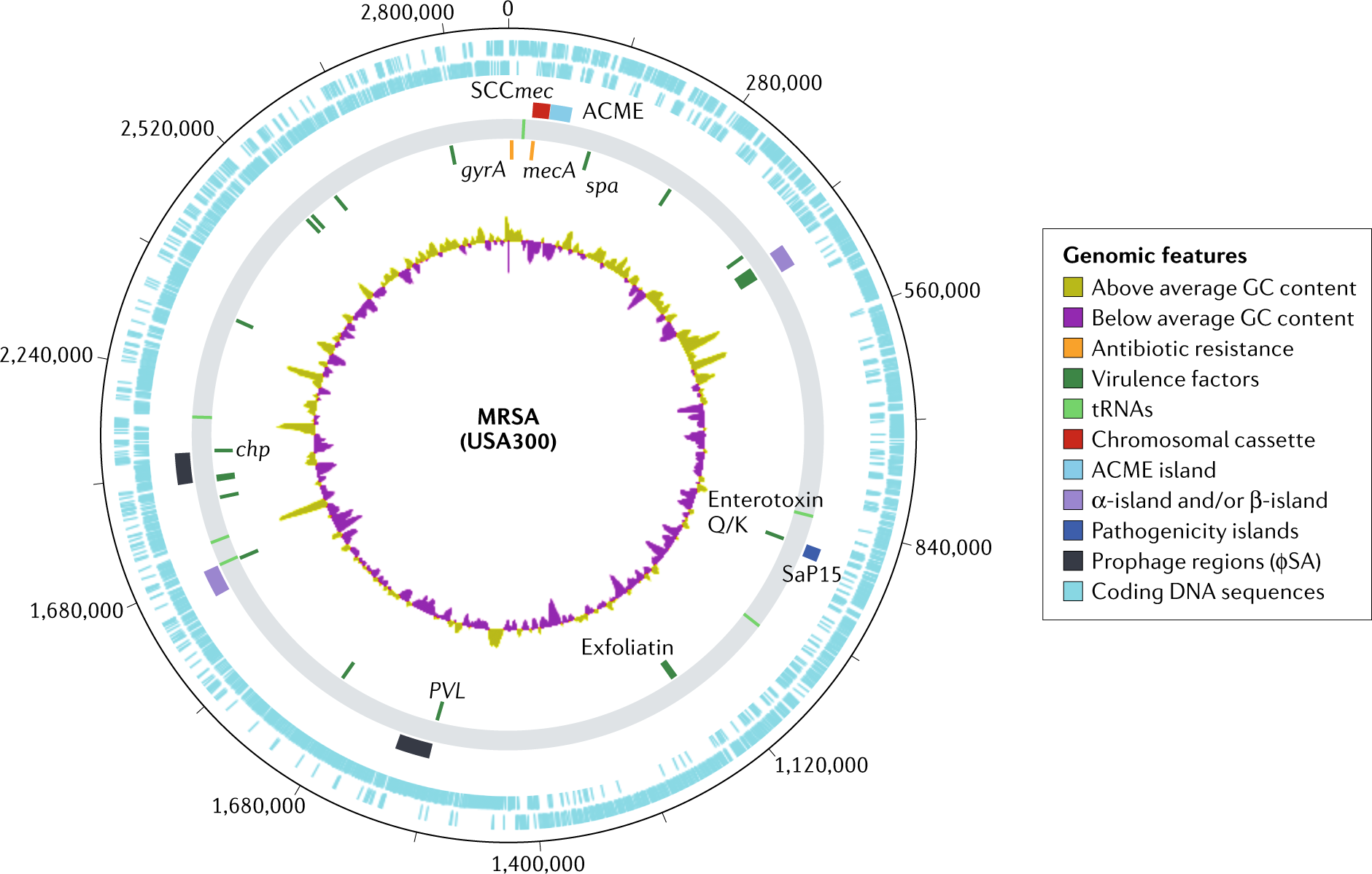
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: an overview of basic and clinical research
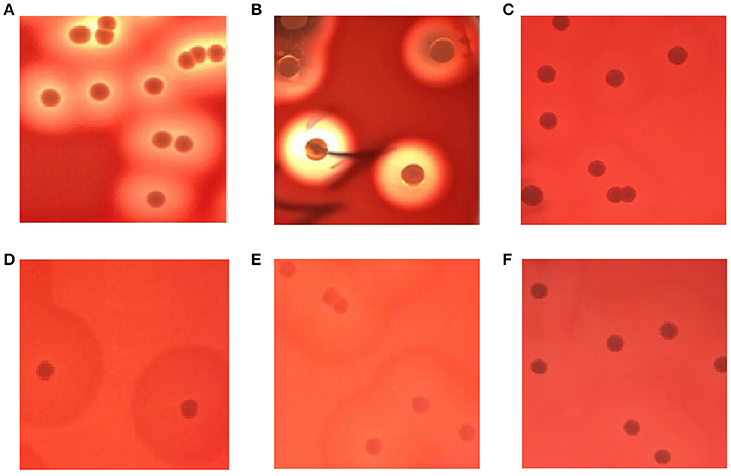
Frontiers Identification and Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Strains with an Incomplete Hemolytic Phenotype

Biofilm-Associated Agr and Sar Quorum Sensing Systems of Staphylococcus aureus Are Inhibited by 3-Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derived from Illicium verum

β-Lactam and glycopeptide antibiotics: first and last line of defense?: Trends in Biotechnology

Glycopeptide Antibiotics
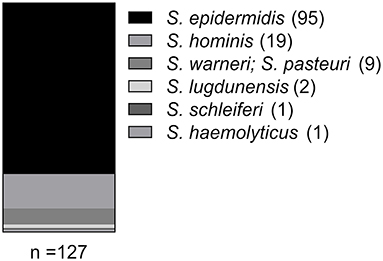
Frontiers Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in Community-Based Healthy Individuals in Germany
The issue beyond resistance: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation is induced by subinhibitory concentrations of cloxacillin, cefazolin, and clindamycin
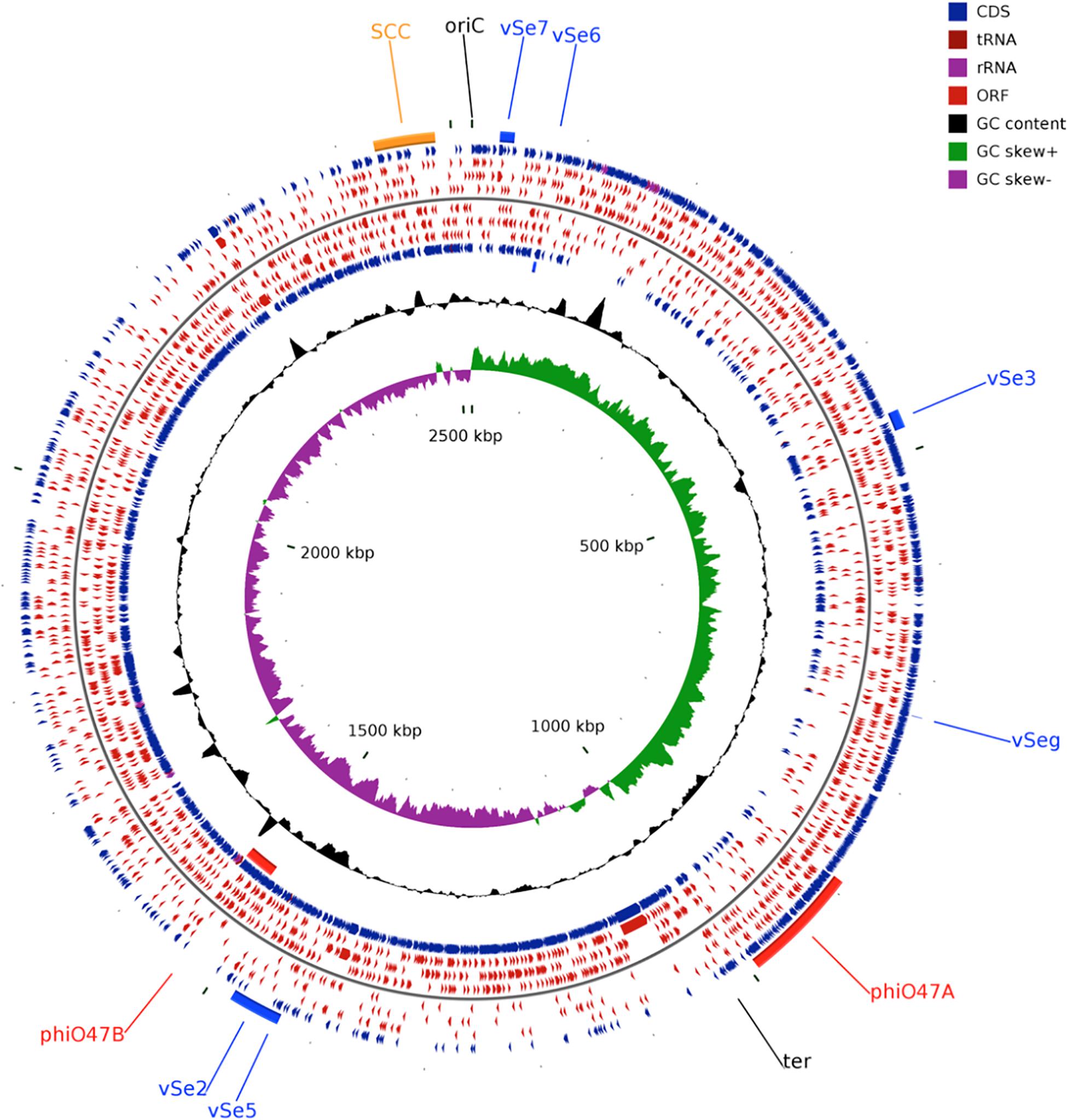
Frontiers The Genome of Staphylococcus epidermidis O47

Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: Trends in Microbiology

Staphylococcus epidermidis bloodstream infections are a cause of septic shock in intensive care unit patients - ScienceDirect

Full article: Increasing prevalence of hypervirulent ST5 methicillin susceptible Staphylococcus aureus subtype poses a serious clinical threat

Antibiotic resistance pattern of Staphylococcus aureus with reference to MRSA isolates from pediatric patients

High Prevalence of Teicoplanin Resistance among Staphylococcus epidermidis Strains in a 5-Year Retrospective Study
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/staph-infections-3156887-FINAL2-48c3a7caea8f429a94f7d074e66d5842.png)