Regulation of MMP-3 expression and secretion by the chemokine eotaxin-1 in human chondrocytes, Journal of Biomedical Science
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Background Osteoarthritis (OA) is characterized by the degradation of articular cartilage, marked by the breakdown of matrix proteins. Studies demonstrated the involvement of chemokines in this process, and some may potentially serve as diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets; however, the underlying signal transductions are not well understood. Methods We investigated the effects of the CC chemokine eotaxin-1 (CCL11) on the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression and secretion in the human chondrocyte cell line SW1353 and primary chondrocytes. Results Eotaxin-1 significantly induced MMP-3 mRNA expression in a dose-dependent manner. Inhibitors of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and p38 kinase were able to repress eotaxin-1-induced MMP-3 expression. On the contrary, Rp-adenosine-3',5'-cyclic monophosphorothioate (Rp-cAMPs), a competitive cAMP antagonist for cAMP receptors, and H-89, a protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor, markedly enhanced eotaxin-1-induced MMP-3 expression. These results suggest that MMP-3 expression is specifically mediated by the G protein-coupled eotaxin-1 receptor activities. Interestingly, little amount of MMP-3 protein was detected in the cell lysates of eotaxin-1-treated SW1353 cells, and most of MMP-3 protein was in the culture media. Furthermore we found that the eotaxin-1-dependent MMP-3 protein secretion was regulated by phospholipase C (PLC)-protein kinase C (PKC) cascade and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)/mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways. These data indicate a specific regulation of MMP-3 secretion also by eotaxin-1 receptor activities. Conclusions Eotaxin-1 not only induces MMP-3 gene expression but also promotes MMP-3 protein secretion through G protein-coupled eotaxin-1 receptor activities. Chemokines, such as eotaxin-1, could be a potential candidate in the diagnosis and treatment of arthritis.
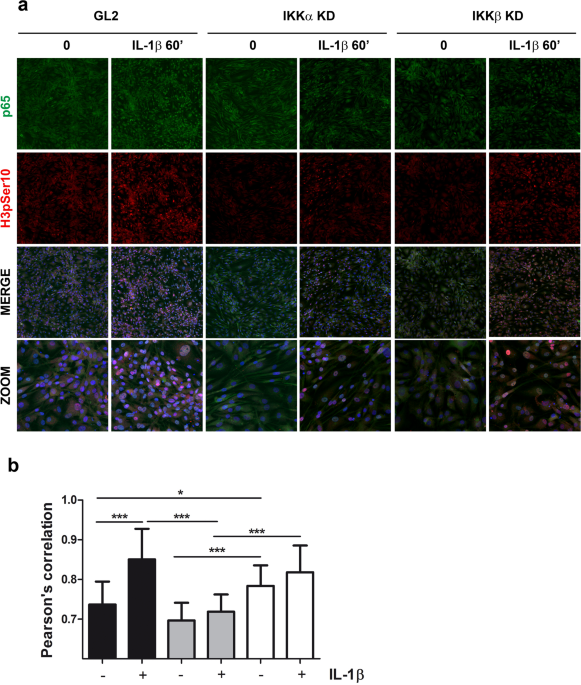
Basal and IL-1β enhanced chondrocyte chemotactic activity on monocytes are co-dependent on both IKKα and IKKβ NF-κB activating kinases

TGF-β inhibits IL-1β-activated PAR-2 expression through multiple pathways in human primary synovial cells, Journal of Biomedical Science
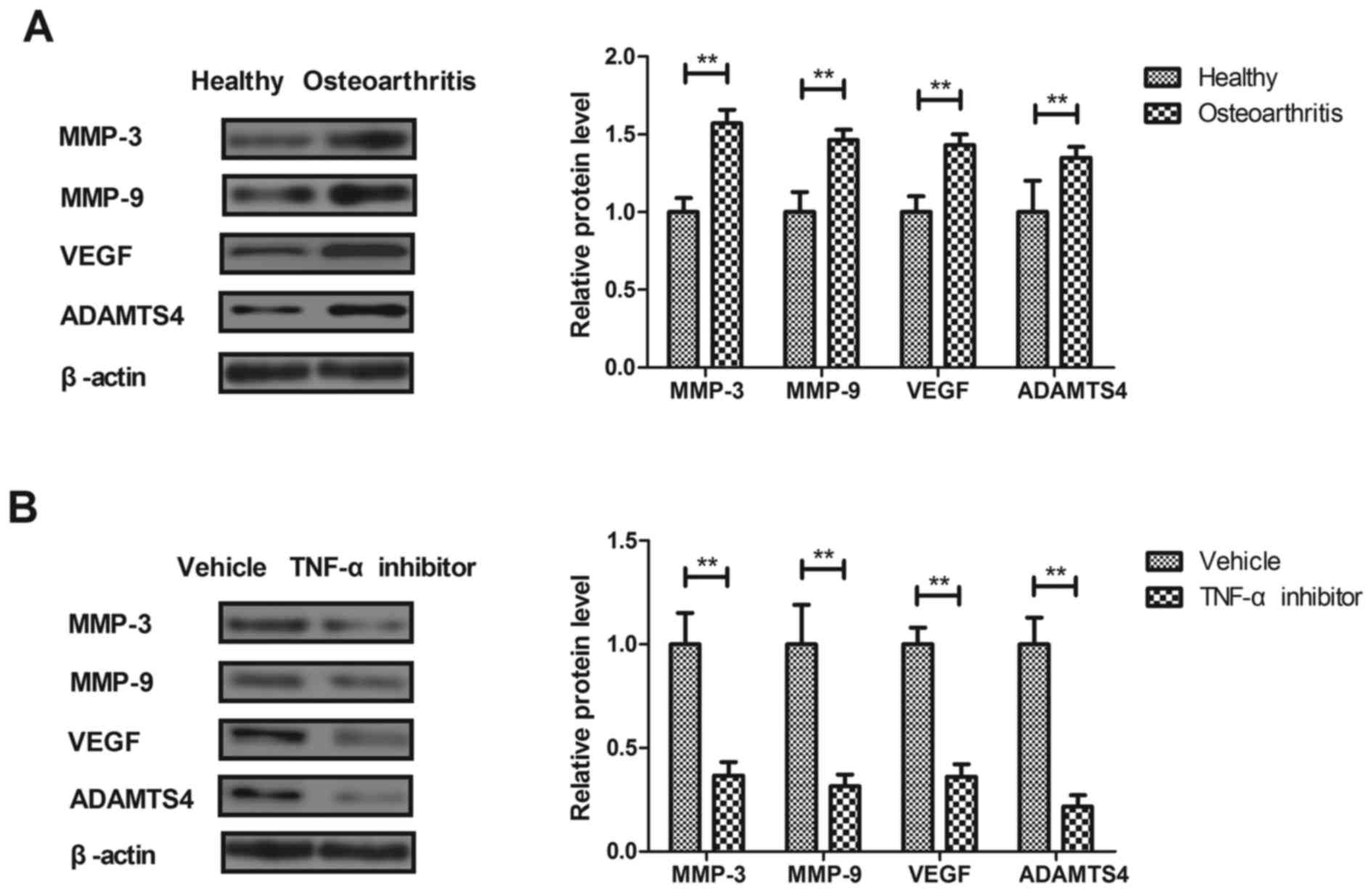
TNF‑α increases the expression of inflammatory factors in synovial fibroblasts by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway in a rat model of monosodium iodoacetate‑induced osteoarthritis

Eotaxin-1 promotes prostate cancer cell invasion via activation of the CCR3-ERK pathway and upregulation of MMP-3 expression

Potential roles of cytokines and chemokines in human intervertebral disc degeneration: interleukin-1 is a master regulator of catabolic processes - ScienceDirect
IJMS June-1 2023 - Browse Articles

Response of Endothelial Cells to Gelatin-Based Hydrogels

Synovial Fluid Eotaxin-1 Levels May Reflect Disease Progression in Primary Knee Osteoarthritis Among Elderly Han Chinese: A Cross-Sectional Study - Bei Li, Yi-Li Zhang, Shou-Yi Yu, 2019
IJMS, Free Full-Text
Nanomaterials, Free Full-Text
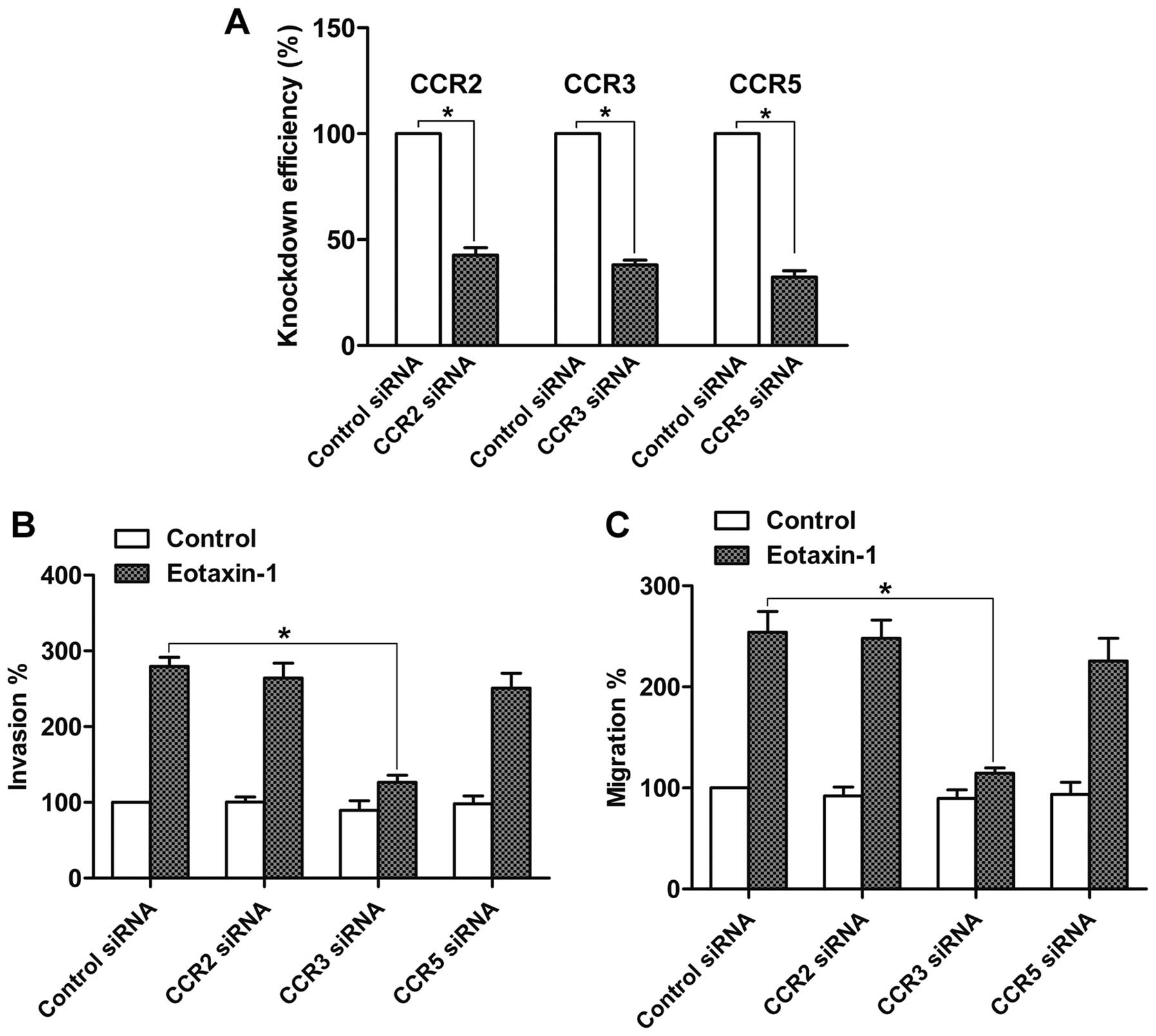
Eotaxin-1 promotes prostate cancer cell invasion via activation of the CCR3-ERK pathway and upregulation of MMP-3 expression

Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Regulation of MMP-3 expression and secretion by the chemokine eotaxin-1 in human chondrocytes, Journal of Biomedical Science