Syndecan-3 is selectively pro-inflammatory in the joint and contributes to antigen-induced arthritis in mice, Arthritis Research & Therapy
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Introduction Syndecans are heparan sulphate proteoglycans expressed by endothelial cells. Syndecan-3 is expressed by synovial endothelial cells of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients where it binds chemokines, suggesting a role in leukocyte trafficking. The objective of the current study was to examine the function of syndecan-3 in joint inflammation by genetic deletion in mice and compare with other tissues. Methods Chemokine C-X-C ligand 1 (CXCL1) was injected in the joints of syndecan-3−/−and wild-type mice and antigen-induced arthritis performed. For comparison chemokine was administered in the skin and cremaster muscle. Intravital microscopy was performed in the cremaster muscle. Results Administration of CXCL1 in knee joints of syndecan-3−/−mice resulted in reduced neutrophil accumulation compared to wild type. This was associated with diminished presence of CXCL1 at the luminal surface of synovial endothelial cells where this chemokine clustered and bound to heparan sulphate. Furthermore, in the arthritis model syndecan-3 deletion led to reduced joint swelling, leukocyte accumulation, cartilage degradation and overall disease severity. Conversely, CXCL1 administration in the skin of syndecan-3 null mice provoked increased neutrophil recruitment and was associated with elevated luminal expression of E-selectin by dermal endothelial cells. Similarly in the cremaster, intravital microscopy showed increased numbers of leukocytes adhering and rolling in venules in syndecan-3−/−mice in response to CXCL1 or tumour necrosis factor alpha. Conclusions This study shows a novel role for syndecan-3 in inflammation. In the joint it is selectively pro-inflammatory, functioning in endothelial chemokine presentation and leukocyte recruitment and cartilage damage in an RA model. Conversely, in skin and cremaster it is anti-inflammatory.

Syndecans Circulation Research

New potential therapeutic approaches targeting synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis - ScienceDirect

Synovial tissues concentrate secreted APRIL – topic of research paper in Clinical medicine. Download scholarly article PDF and read for free on CyberLeninka open science hub.

Matrix Metalloproteinases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Pharmacology

Full article: ISEV2018 abstract book
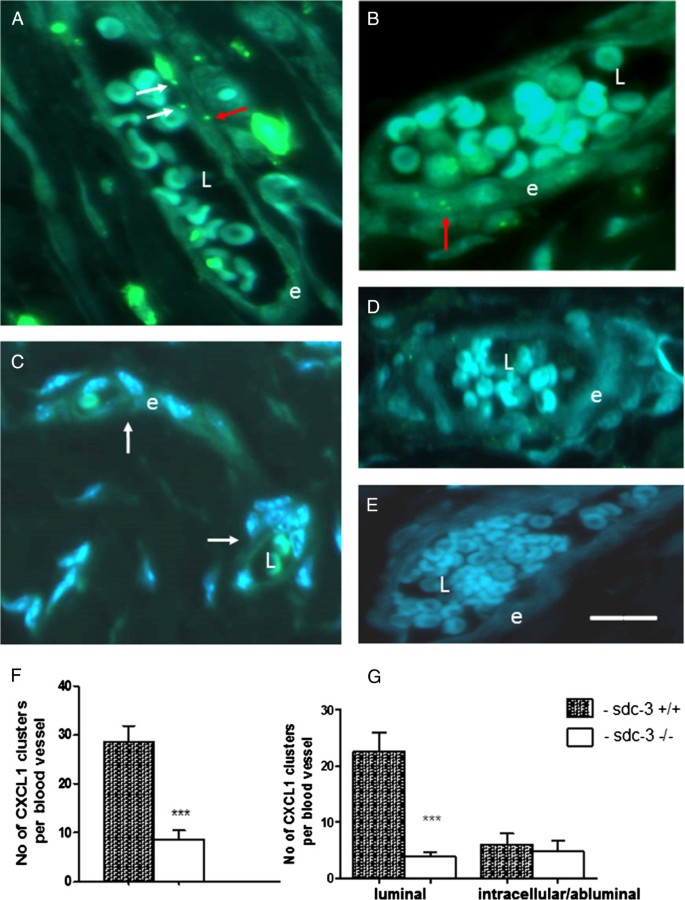
Syndecan-3 is selectively pro-inflammatory in the joint and contributes to antigen-induced arthritis in mice, Arthritis Research & Therapy

Mouse Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis - P. Caplazi, M. Baca, K. Barck, R. A. D. Carano, J. DeVoss, W. P. Lee, B. Bolon, L. Diehl, 2015

EP2420250A1 - Anti-Syndecan-4 antibodies - Google Patents

Cartilage extracellular matrix-derived matrikines in osteoarthritis
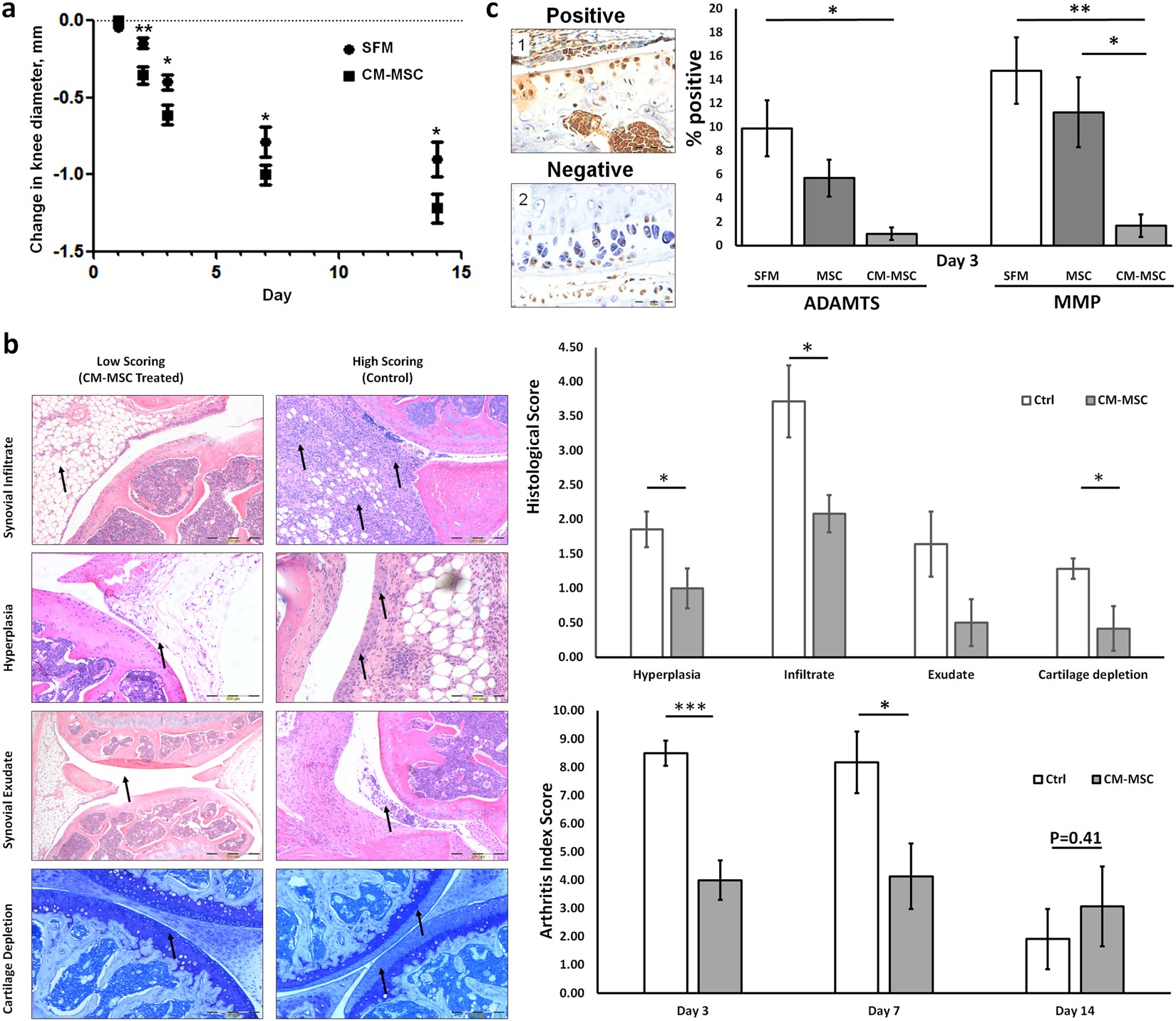
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Reduces Disease Severity and Immune Responses in Inflammatory Arthritis
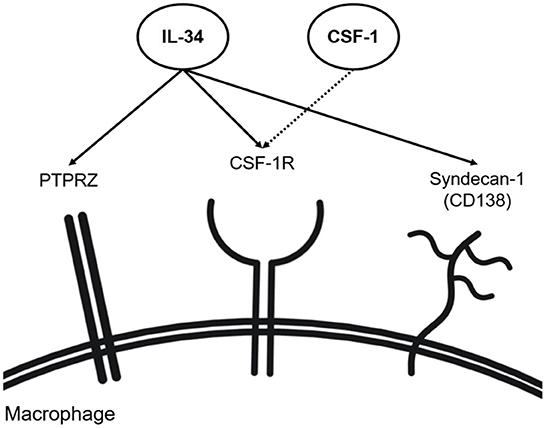
Frontiers Interleukin-34-regulated T-cell responses in rheumatoid arthritis

Effect of Polarization and Chronic Inflammation on Macrophage Expression of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Biosynthesis Enzymes - Maarten Swart, Linda Troeberg, 2019







