Sustainability, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
The bioeconomy has gained traction among the broader discourses on sustainable development, ecological transition, and the circular economy. Governments in the Global North and international institutions maintain that the bioeconomy can gradually replace fossil-based raw materials and nonrenewable resources with biomass and biological renewables. The Global South has increasingly adopted the approach, but with important variations across mega-biodiverse regions. In these regions, the bioeconomy must encourage economic activities that preserve biodiversity and strengthen local communities, promoting their well-being and cultural diversity. This paper argues that conventional research methods and indicators are not fit for this purpose. We therefore propose an alternative method and indicators and present an initial validation of the approach with an application to the pirarucu (Arapaima gigas) value chain in the Brazilian . By applying a bottom-up approach to evaluation that considers the perspective of the individuals and communities involved, the proposed methodology captures relevant dimensions of the value chain—including trade-offs—while identifying bottlenecks and the role of institutions. It also allows for verification of the achievement of the objectives of the socio-biodiversity bioeconomy in this model. The application to the case study finds that the managed pirarucu fisheries are a viable value chain associated with improved fish stocks and lower than average forest loss. Socio-economic benefits include the generation of reasonable income and greater participation by women. Income remains a complement to other sources of livelihood, however, and attractiveness to local communities is an issue. Positive outcomes are owed largely to local knowledge, collective action, and the role played by meta-organizations, while negative ones such as overfishing have resulted from institutional failures. Conventional analysis would likely not have considered these factors and missed these policy lessons. This corroborates the view that alternative methods and indicators are needed for the socio-biodiversity bioeconomy. While the application to the case study suggests the method and the indicators are conceptually suitable, we identify a number of shortcomings regarding the identification of interventions, attribution, and monitoring of the sustainability of the model.

Sustainability A Comprehensive Foundation 45.1 PDF, PDF, Sustainability

Sustainability, Free Full-Text, Place Branding and Urban Regeneration as Dialectical Processes in Local Development Pl…

openLCA is a free, professional Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and footprint software with a broad range of features and many available databases, created by GreenDelta since 2006

Sustainable Production and Consumption, Journal

Energy Efficiency & Sustainability Experts
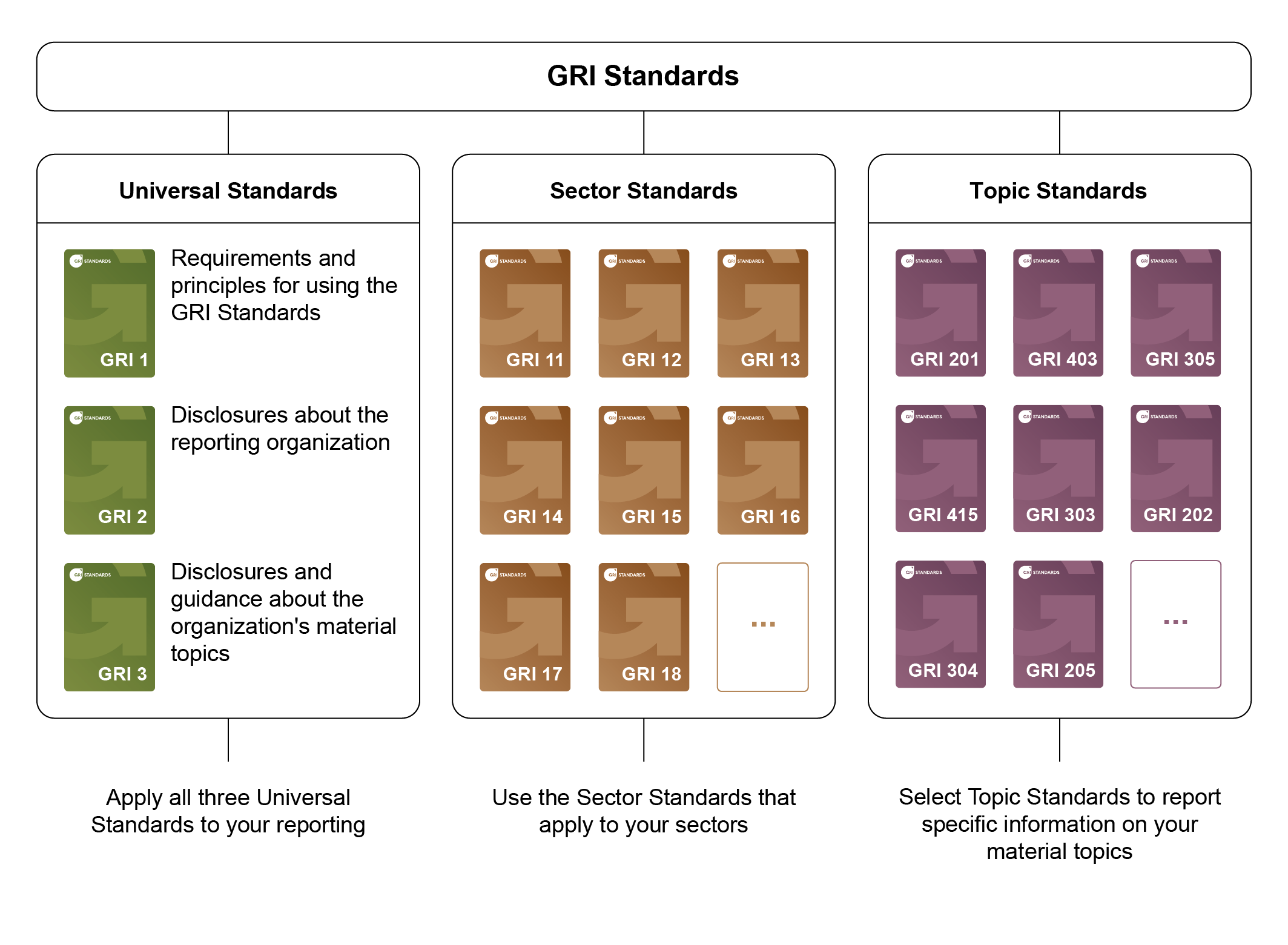
GRI - Standards

Sustainability, Free Full-Text, Train-Induced Building Vibration and Radiated Noise by Considering S…
Sustainability png word sticker typography

What are the Three Pillars of Sustainable Development?

Sustainability, Free Full-Text, Urban Housing Density and Infrastructure Costs
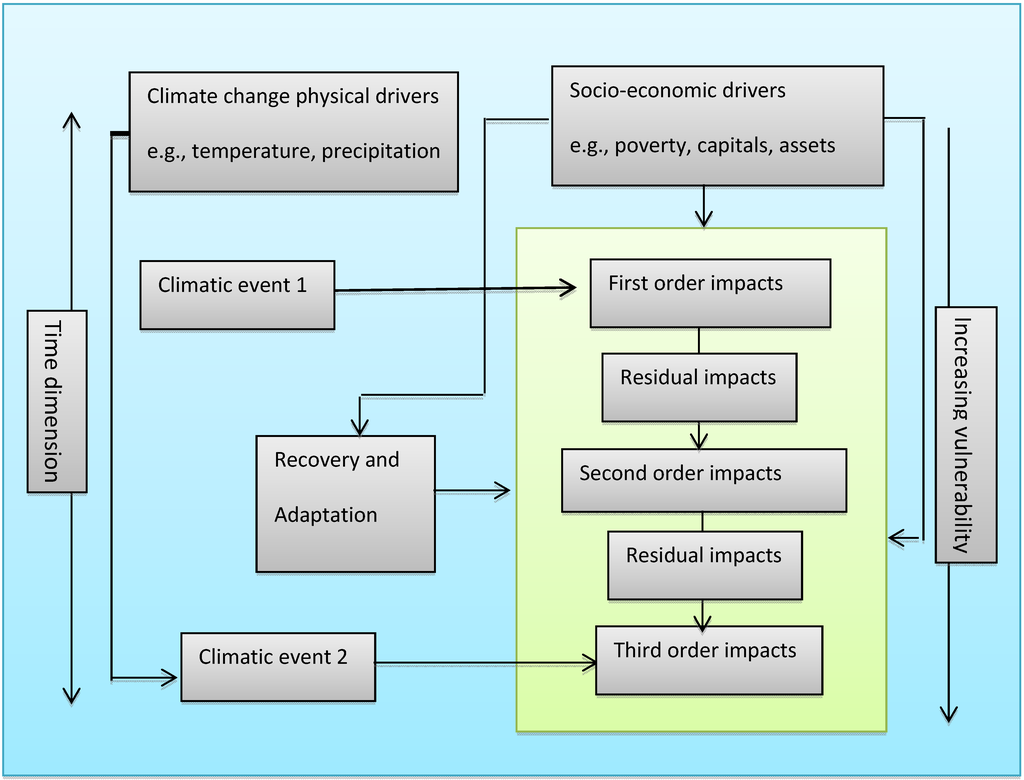
Sustainability, Free Full-Text







