Pathogens, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Understanding Legionella survival mechanisms within building water systems (BWSs) is challenging due to varying engineering, operational, and water quality characteristics unique to each system. This study aimed to evaluate Legionella, mycobacteria, and free-living amoebae occurrence within a BWS over 18–28 months at six locations differing in plumbing material and potable water age, quality, and usage. A total of 114 bulk water and 57 biofilm samples were analyzed. Legionella culturability fluctuated seasonally with most culture-positive samples being collected during the winter compared to the spring, summer, and fall months. Positive and negative correlations between Legionella and L. pneumophila occurrence and other physiochemical and microbial water quality parameters varied between location and sample types. Whole genome sequencing of 19 presumptive Legionella isolates, from four locations across three time points, identified nine isolates as L. pneumophila serogroup (sg) 1 sequence-type (ST) 1; three as L. pneumophila sg5 ST1950 and ST2037; six as L. feeleii; and one as Ochrobactrum. Results showed the presence of a diverse Legionella population with consistent and sporadic occurrence at four and two locations, respectively. Viewed collectively with similar studies, this information will enable a better understanding of the engineering, operational, and water quality parameters supporting Legionella growth within BWSs.
Melanins in fungal pathogens
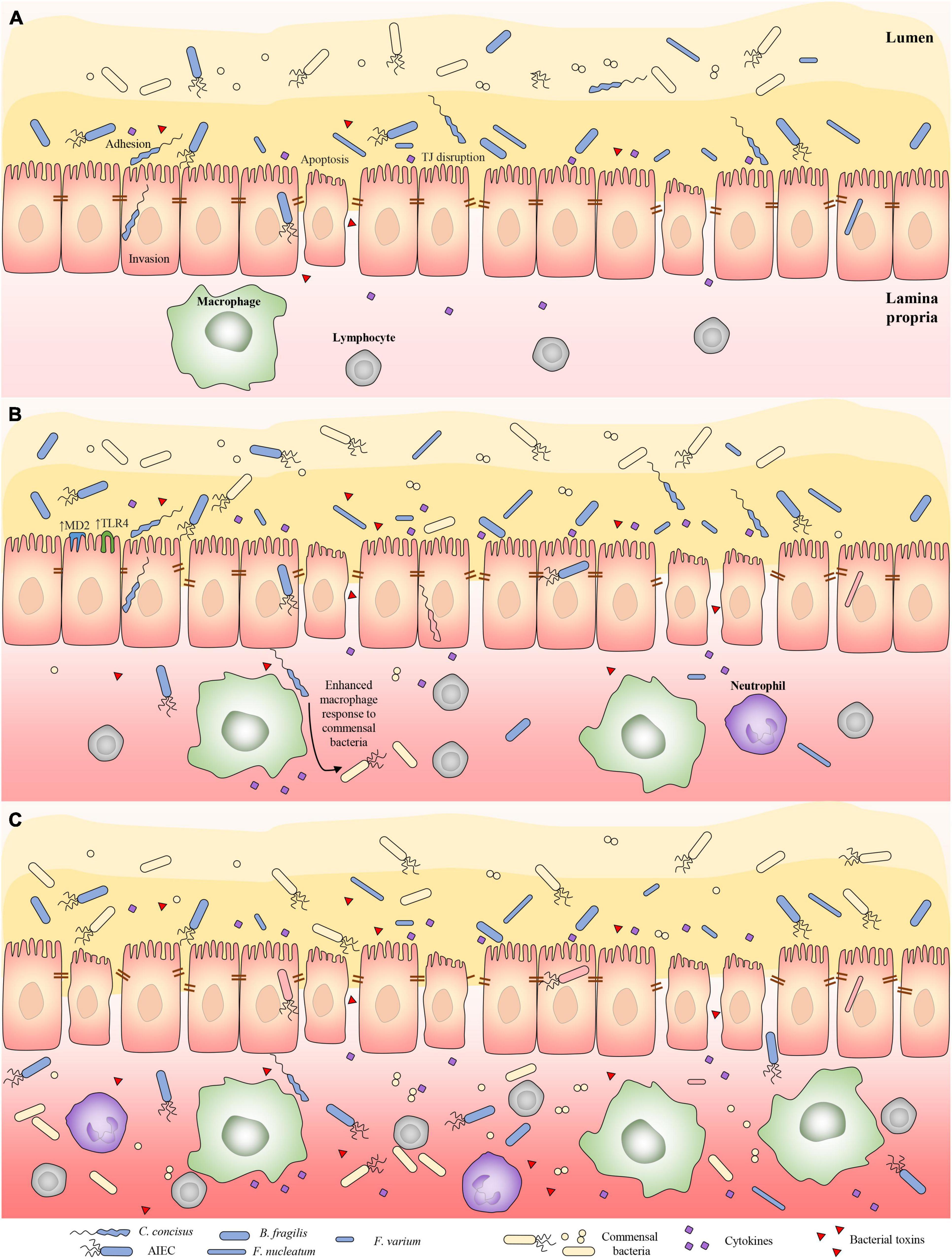
Frontiers Bacterial Species Associated With Human Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Their Pathogenic Mechanisms
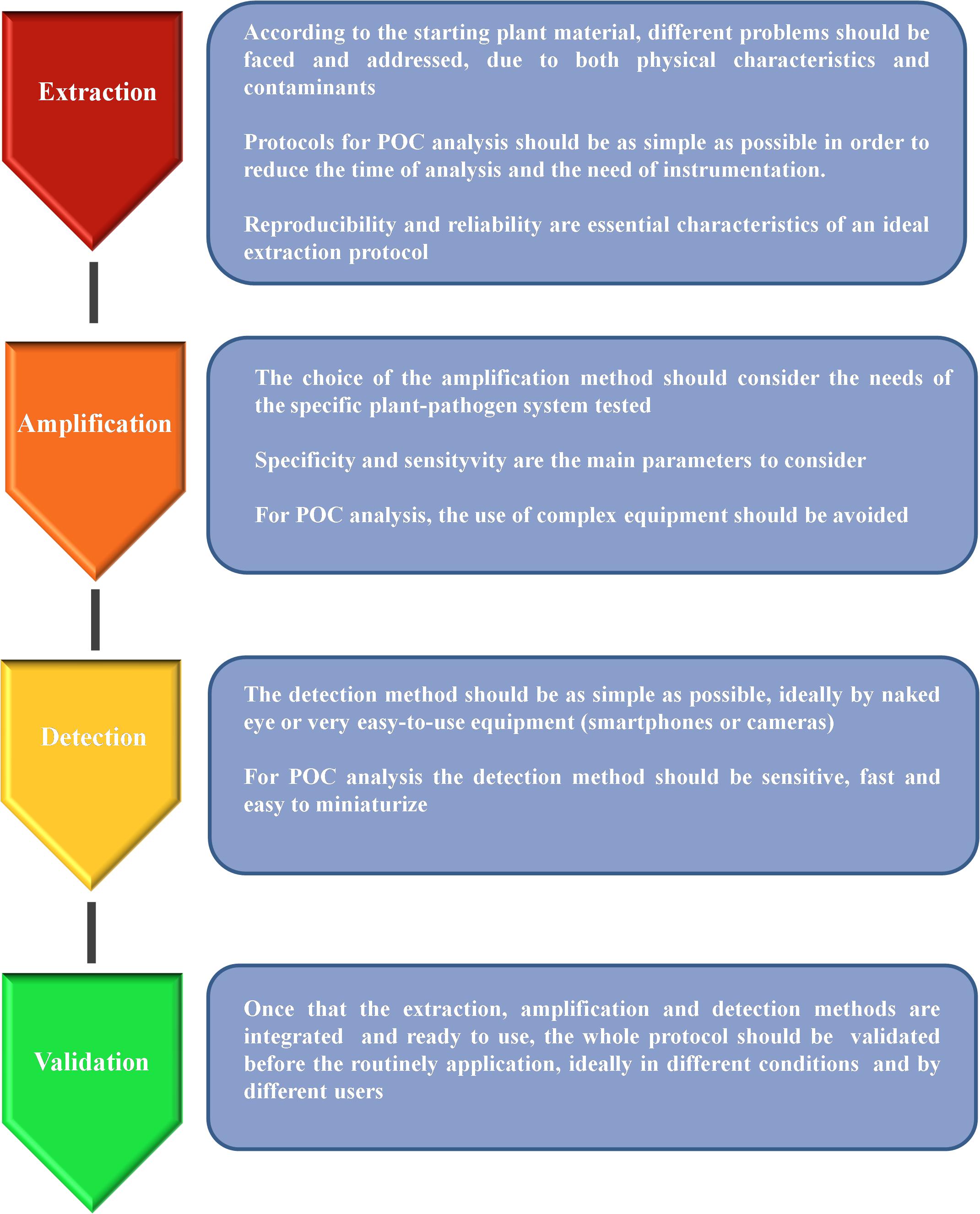
Frontiers Molecular Approaches for Low-Cost Point-of-Care Pathogen Detection in Agriculture and Forestry

Microbial Minimalism: Genome Reduction in Bacterial Pathogens - ScienceDirect

Pathogens, Definition, Types & Examples - Video & Lesson Transcript

Protein Science: Vol 32, No 12

Pathogenic bacteria - Wikipedia
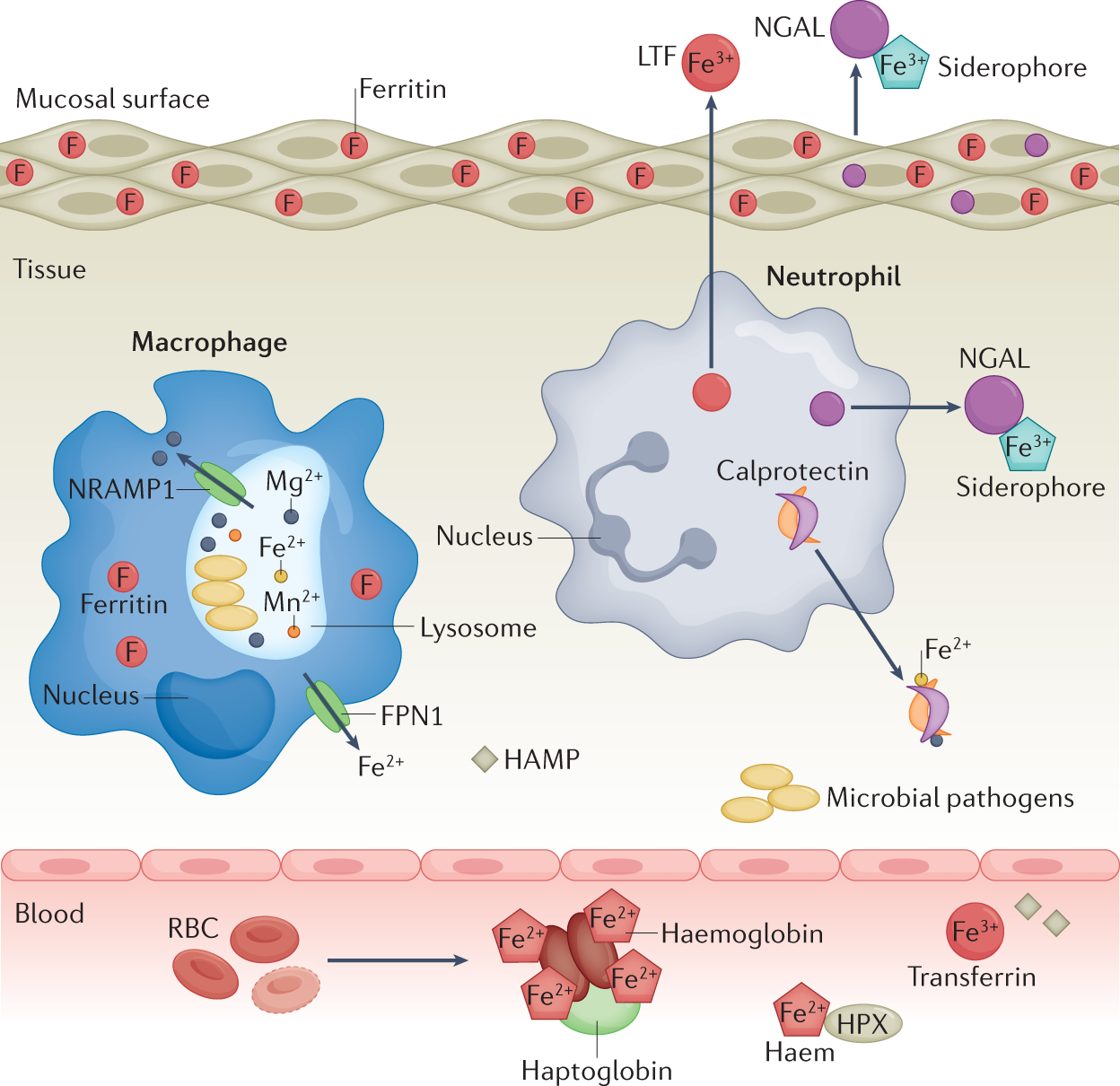
Nutritional immunity: the battle for nutrient metals at the host–pathogen interface
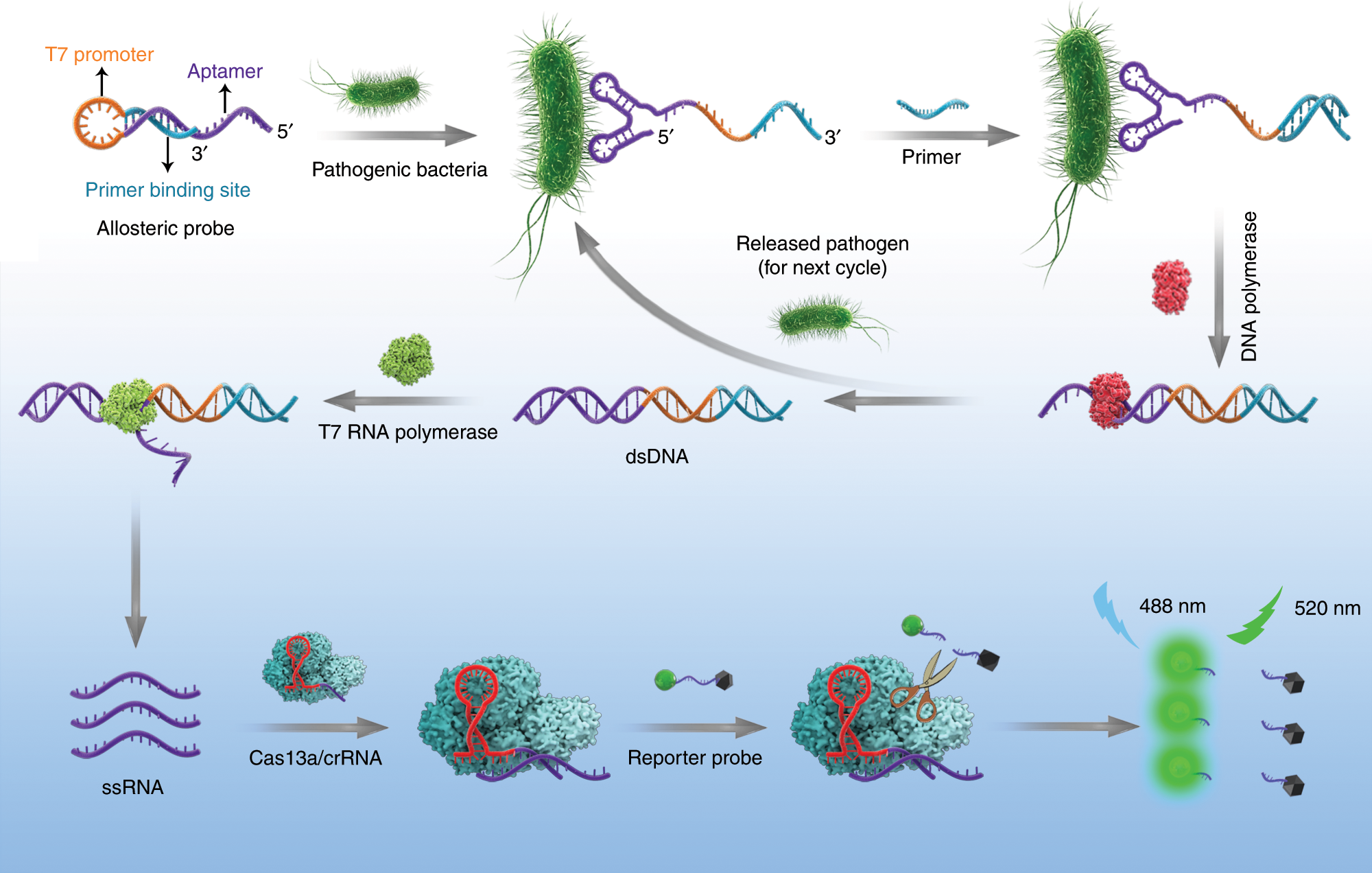
Sensitive detection of a bacterial pathogen using allosteric probe-initiated catalysis and CRISPR-Cas13a amplification reaction
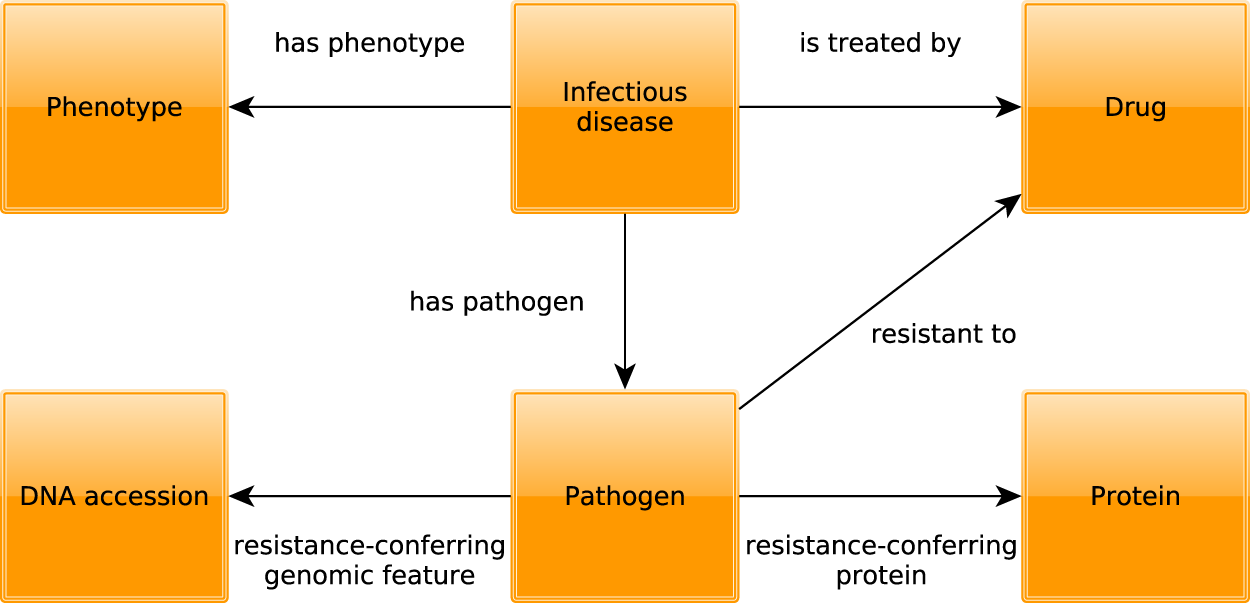
PathoPhenoDB, linking human pathogens to their phenotypes in support of infectious disease research

ThinkLite Natick MA

What is a pathogen? - 4-H Animal Science

Pathogens and Disease Word Search - WordMint

Sequential Infection with Common Pathogens Promotes Human-like Immune Gene Expression and Altered Vaccine Response - ScienceDirect

NADases as weapons for both plant pathogens and their hosts






