Our Next Course + The Ultimate Chess Openings Guide for Beginners - Remote Chess Academy
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
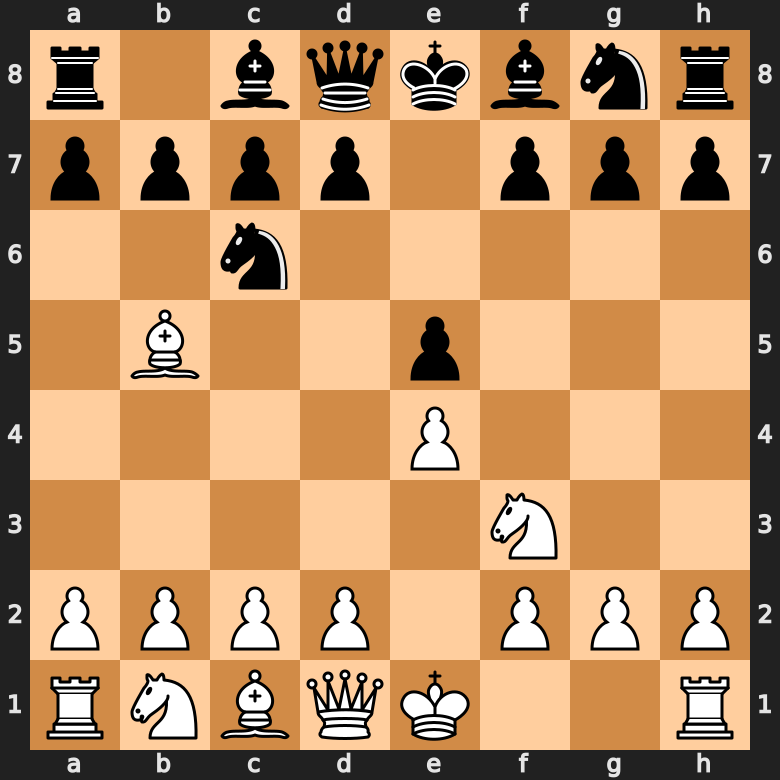
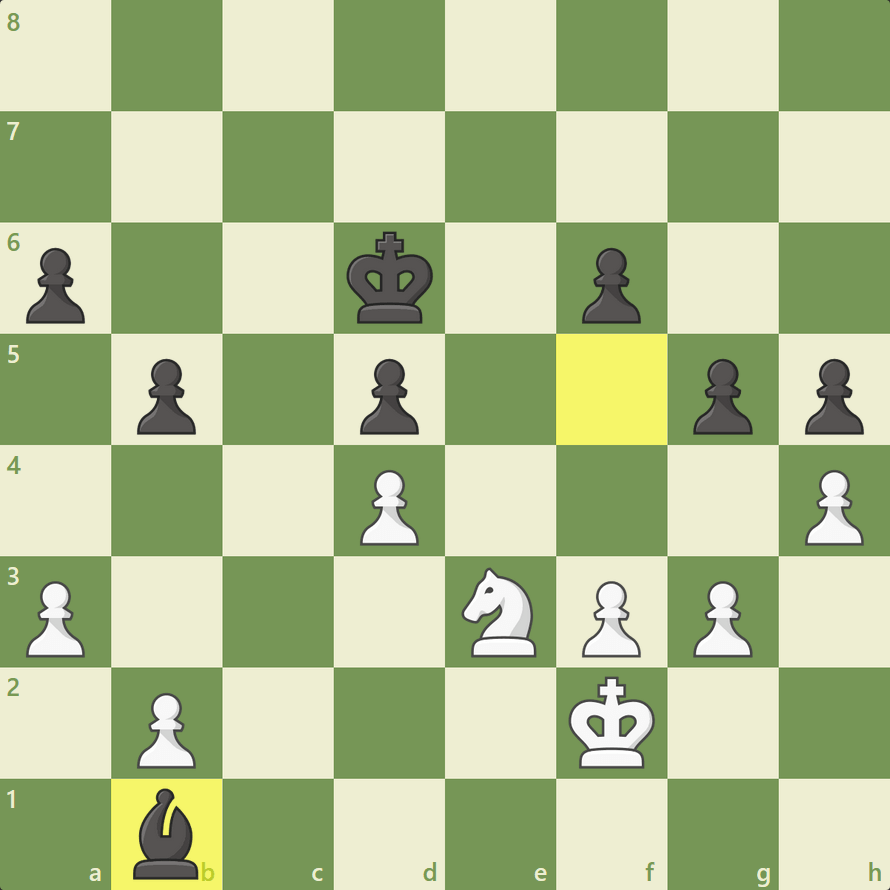
Over the last few months, we’ve been working on a new course based on YOUR needs. For those of you who took the time to take our surveys or who provide regular feedback about their progress roadblocks, we thank you! 😊 If you want to get notified when we launch the course, sign up here and you’ll hear from us right after my new course is launched. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Chess Openings Welcome to the ultimate beginner’s guide to chess openings! In this guide, we will explore the fundamental chess opening principles that will help you establish a strong foundation in chess openings. By understanding these principles, you can gain an advantage over your opponents right from the start. Below, you can find the examples shown in the video: Rule-1: Controlling the Center In chess, the center of the board holds immense importance. By controlling the central squares, you gain control over the game. The four central squares, located in the middle of the board, are vital for your strategy. To establish control, focus on pushing your central pawns forward, such as 1.d4. By doing so, you not only secure the center but also create opportunities to dominate the game early on. Occupying the center enables your pawns and other pieces to control essential lines and diagonals, giving you a significant advantage. Rule-2: Developing Your Pieces Quickly Another crucial aspect of chess openings is developing your minor pieces (knights and bishops) rapidly. By doing this, you ensure that your pieces are active and ready for action. The general rule is to prioritize piece development over other considerations. However, be cautious of potential pitfalls, as your opponent may tempt you into making reactive moves that deviate from sound opening principles. Sometimes, it might be handy to sacrifice a pawn (gambit) in order to get the initiative and be ahead of your opponent in development. For example, after 1.e4 d5 2.exd5 Nxf6. Here, you don’t cature the pawn back as Black, but just continue to develop. And when they support the pawn with 3.c4, you can get ahead in development with 3…c6 4.dxc6 Nxc6. Now Black already has a couple of pieces developed, while White is completely passive. Rule-3: Castling Early (within 5-10 moves) Castling is a vital move to ensure the safety of your king and activate your rooks. Ideally, you should castle within the first five moves, or at least within the first ten moves. By castling, you protect your king from potential threats and position your rooks for improved coordination. Remember, a well-castled king is more secure and allows you to shift your focus towards strategic maneuvering. For example, White castles in just 4 moves in the Ruy Lopez opening after 1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bb5 Nf6 4.0-0. Rule-4: Seizing the Initiative Seizing the initiative means taking proactive measures to create threats and put pressure on your opponent. By developing your pieces and creating small tactical opportunities, you force your opponent to react and make defensive moves. This places you in a favorable position, allowing you to gradually build your attack and maintain control of the game. A great example for this is the Rousseau Gambit, where Black forces the White knight to back to g1 after 1.e4 e5 2.Nf3 Nc6 3.Bc4 f5 4.exf5 e4. And you can continue to push White back after 5.Ng1 d5, forcing the bishop to go back. Initiating threats not only disrupts your opponent’s plans but also forces them to play defensively, limiting their options. Rule-5: Understanding Your Opponent’s Moves While focusing on your own strategy, it is equally important to pay attention to your opponent’s moves. By understanding the intentions behind their moves, you can anticipate their plans and potential threats. Avoid falling into traps or blunders by critically analyzing your opponent’s moves and asking “Why did they play this move?“. Remember, every move made by your opponent carries a purpose, and by grasping their intentions, you can make informed decisions and respond effectively. Here’s an instructive example from the Caro-Kann Defense. 1.e4 c6 2.d4 d5 3.Bd3 Nf6 4.e5 Nd7 5.e6. A lot of players react quickly without thinking by playing 5…fxe6. And that leads to a quick checkmate after 6.Qh5+ g6 7.Qxg6+ hxg6 8.Bxg6#. Had Black thought about why White sacrificed that pawn, they wouldn’t have gotten checkmated. Conclusion Chess openings lay the foundation for a successful game. By adhering to these fundamental principles, you can enhance your chess skills and gain an advantage over your adversaries. Remember, this blog-post provides a brief overview, and for a more comprehensive understanding, make sure to watch our complete video lesson with instructive examples. So, get ready to master the art of chess openings and take your game to new heights!
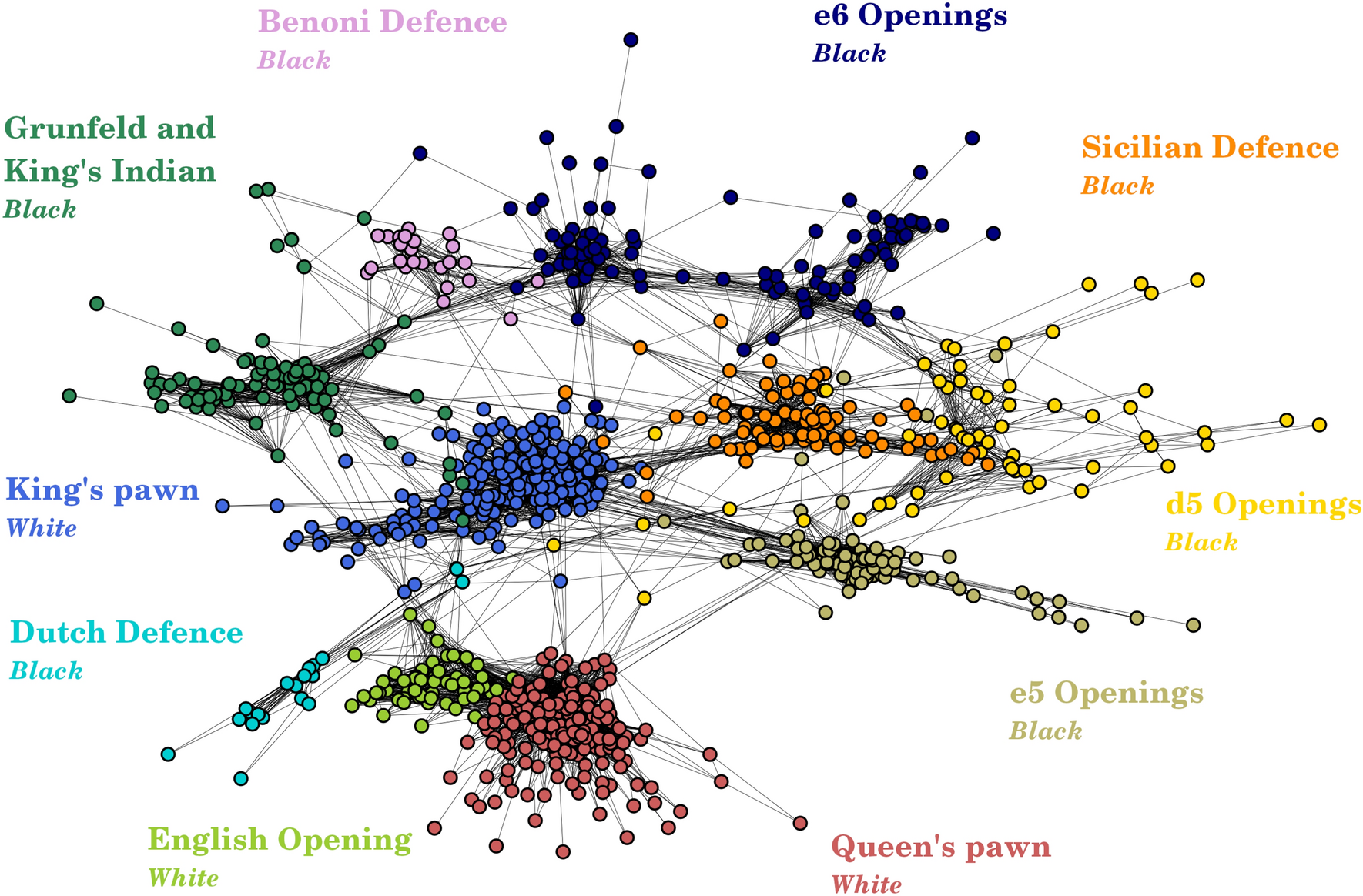
Quantifying the complexity and similarity of chess openings using online chess community data

TRICKY Chess Opening for Black [It Works Against 1.e4 & 1.d4] - Remote Chess Academy

iCore Electronic Chess Set - Brain Power Training with Talking Tutor and Challenging Games - Perfect for Kids and Family Fun : Toys & Games

Remote Chess Academy

How to Castle in Chess: Rules & Strategies

chess openings for beginners: The Ultimate Guide To Learn Chess Board Rules And Start Winning Using The Best Strategies and Most Efficient Tactics.: Alex Queen: 9781802236408: : Books

Best Chess Podcasts: The Ultimate Guide To Chess Podcasts in 2022 - Chessentials

Best Chess Opening To Win Up To 1900 ELO After 1.e4 [Tricky Gambit]

Winning the Middlegame - A brand new course from GM Igor Smirnov - Remote Chess Academy - Videos - Internet Chess Club

Computer chess - Wikipedia

Remote Chess Academy

Opening – Remote Chess Academy – Shop

I Won 90% Games With This Opening
Chess Opening Moves III –

Chess is surging in popularity among all ages. Here's why