The Dead Sea—environmental research on the edge of extremes
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
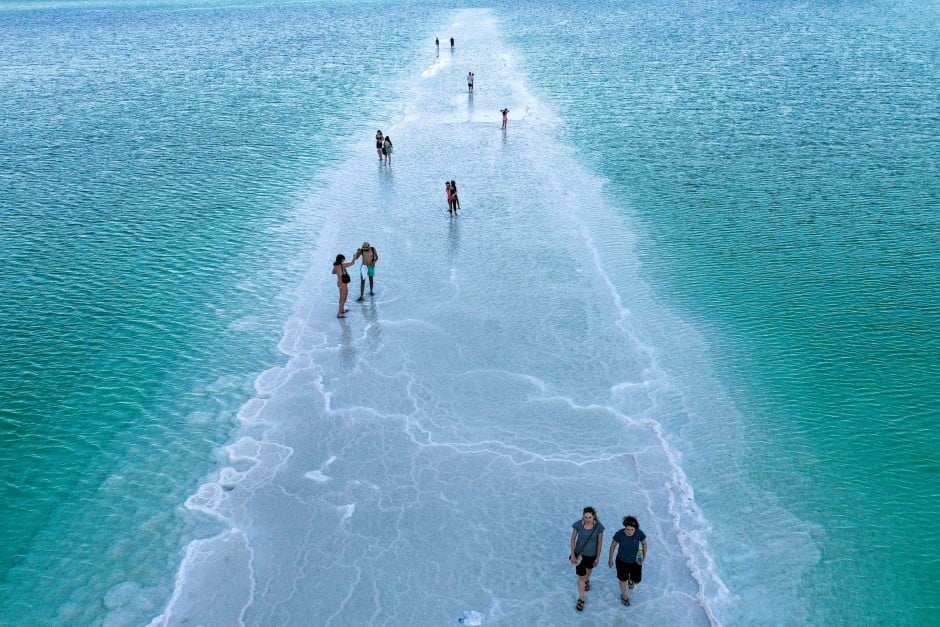
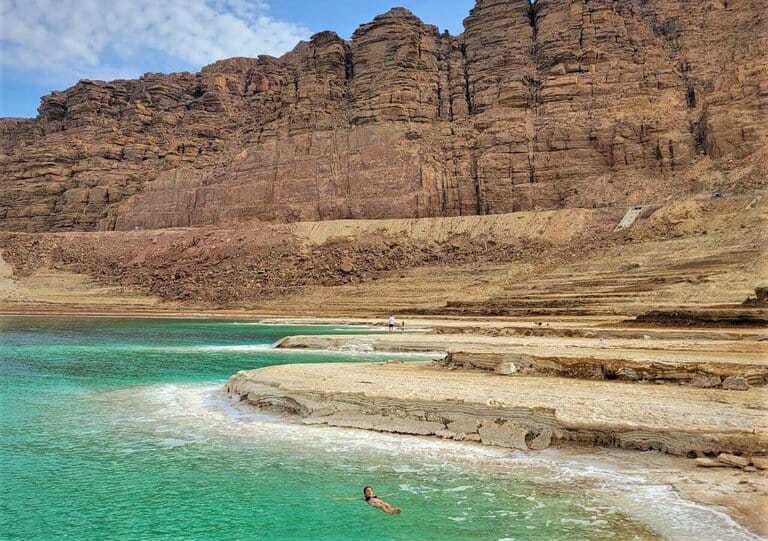
The water level of the Dead Sea drops by more than one meter per year. Thousands of sinkholes, sudden strong rainfall events and flash floods are among others, the challenges facing the population and the environment in the region. The underlying processes were studied by scientists from Germany, Israel, Jordan, and Palestine at the DESERVE Helmholtz Virtual Institute; the work was coordinated by the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT). Their findings contribute to prediction models, risk assessments, and adaptation strategies. "Environmental Research on the Edge of Extremes" will be presented by the DESERVE scientists at the closing event in Halle (Saale) on September 12, 2017. The interested public and representatives of the media are cordially invited to attend.

Under the Dead Sea, Warnings of Dire Drought - The Earth Institute - Columbia University
How jelly-like bodies help sea creatures survive extreme conditions - Big Think

New perspectives on interdisciplinary earth science at the Dead Sea: The DESERVE project - ScienceDirect

New Dead Sea Research Institute Opens, The Department of Environmental Studies

Extreme heat and plastic pollution push oceans to brink – DW – 02/11/2022
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1068103764-818e2487ac064b6c89c4758a7ef02903.jpg)
Complete Guide to Visiting the Dead Sea
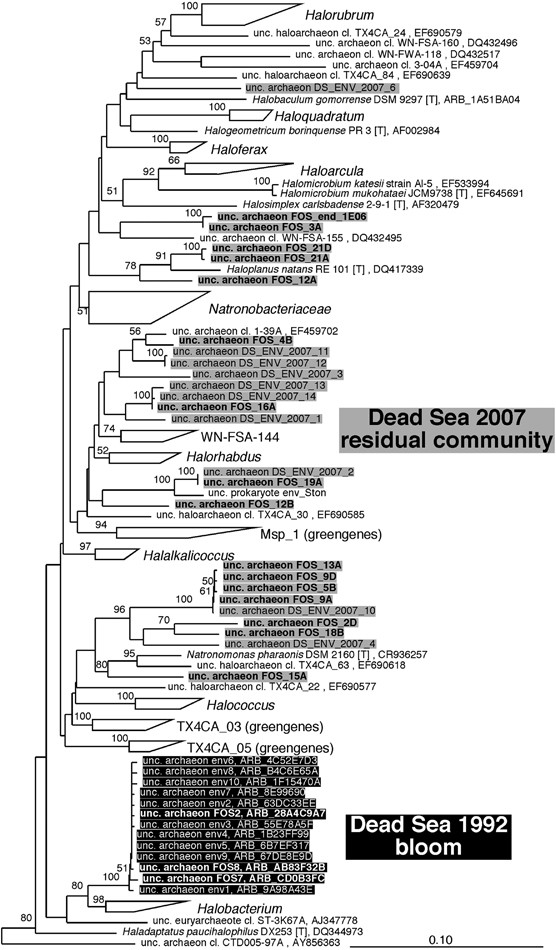
Comparative community genomics in the Dead Sea: an increasingly extreme environment

18 Places Most Affected by Climate Change

Salton Sea - Wikipedia

israel hamas war: Red cow, Life in Dead Sea: Three strange biblical events spark end-of-the-world speculations - The Economic Times
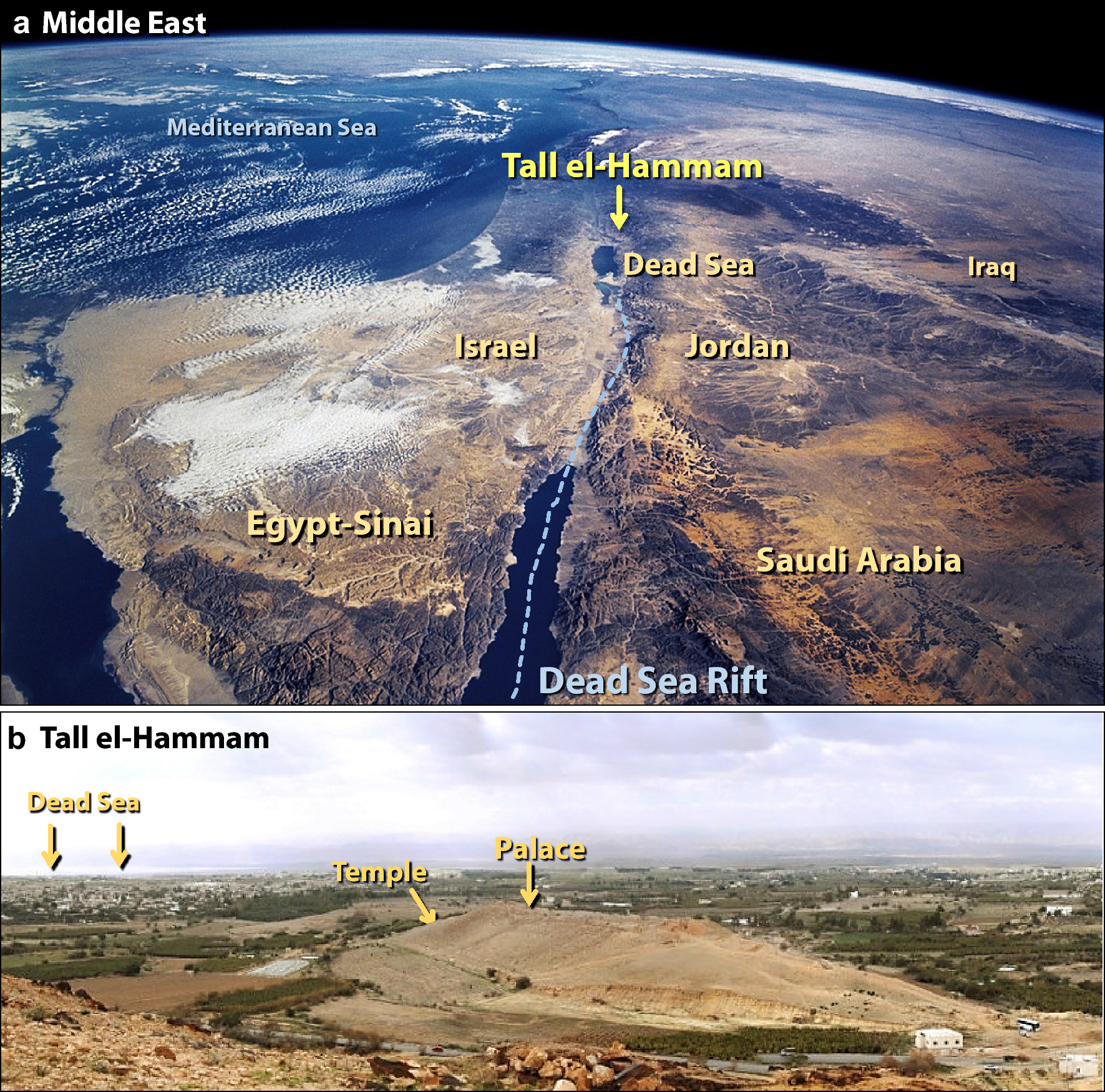
A Tunguska sized airburst destroyed Tall el-Hammam a Middle Bronze Age city in the Jordan Valley near the Dead Sea

Aral Sea, Description, History, Map, Shrinking, & Facts






