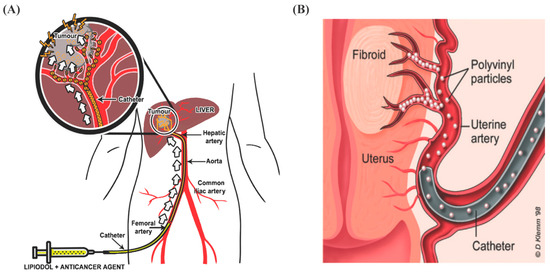
A) Preparation of DC-beads and lipiodol embolic agents currently in
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

Toward a better understanding of the mechanism of action for intra-arterial delivery of irinotecan from DC Bead(TM) (DEBIRI)

Vandetanib-eluting Radiopaque Beads: Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Efficacy in a Rabbit Model of Liver Cancer

Fabrication of radiopaque drug-eluting beads based on Lipiodol/biodegradable-polymer for image-guided transarterial chemoembolization of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma - ScienceDirect
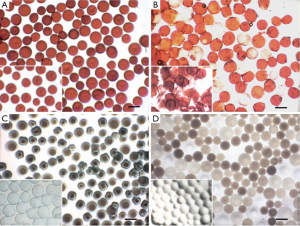
Transcatheter embolization therapy in liver cancer: an update of clinical evidences - Wáng - Chinese Journal of Cancer Research
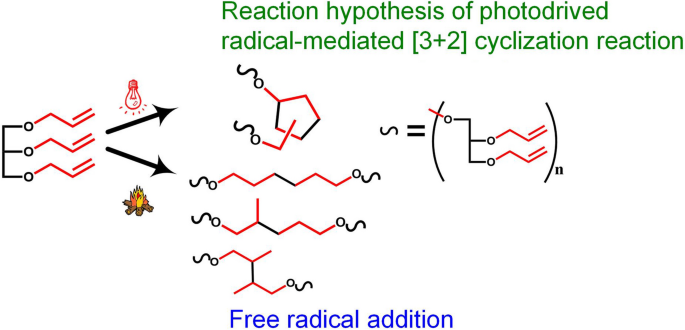
Preparation of the amorphous embolic agents from glyceryl triallyl ether via a photo-driven radical-mediated [3 + 2] cyclopolymerization

Doxorubicin-loaded drug-eluting beads (DC Bead®) for use in transarterial chemoembolization: A stability assessment - Jean-Daniel Hecq, Andrew L Lewis, Danielle Vanbeckbergen, Alexandre Athanosopoulos, Laurence Galanti, Jacques Jamart, Peter Czuczman

PDF] Synthesis of Biocompatible and X-ray Opaque Iodinated Polymeric Microparticles as an Embolic Material

Review of the Development of Methods for Characterization of Microspheres for Use in Embolotherapy: Translating Bench to Cathlab - Caine - 2017 - Advanced Healthcare Materials - Wiley Online Library

Principles of embolization

Effect of Vial shaking on Loading Time of Epirubicin into Drug-Eluting Bead
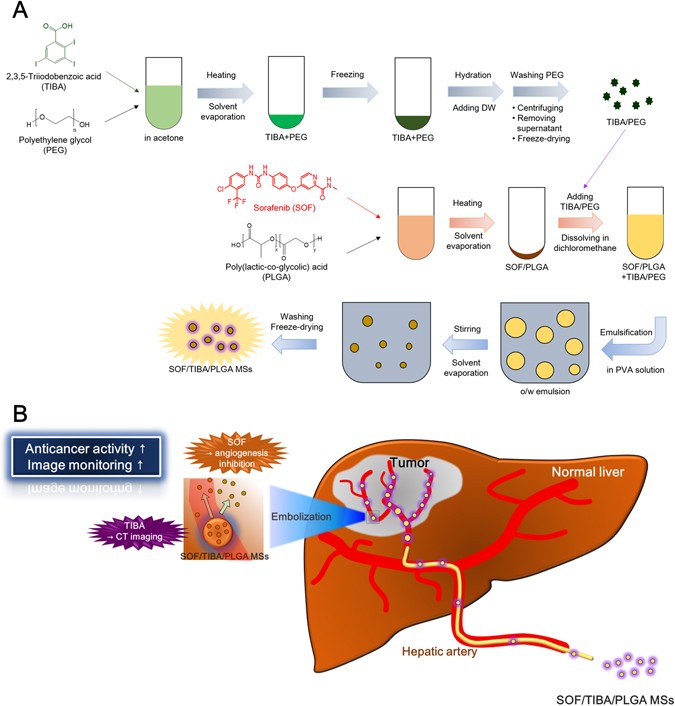
Sorafenib and 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid-loaded imageable microspheres for transarterial embolization of a liver tumor
Biomimetics, Free Full-Text

Full article: DC Bead embolic drug-eluting bead: clinical application in the locoregional treatment of tumours







