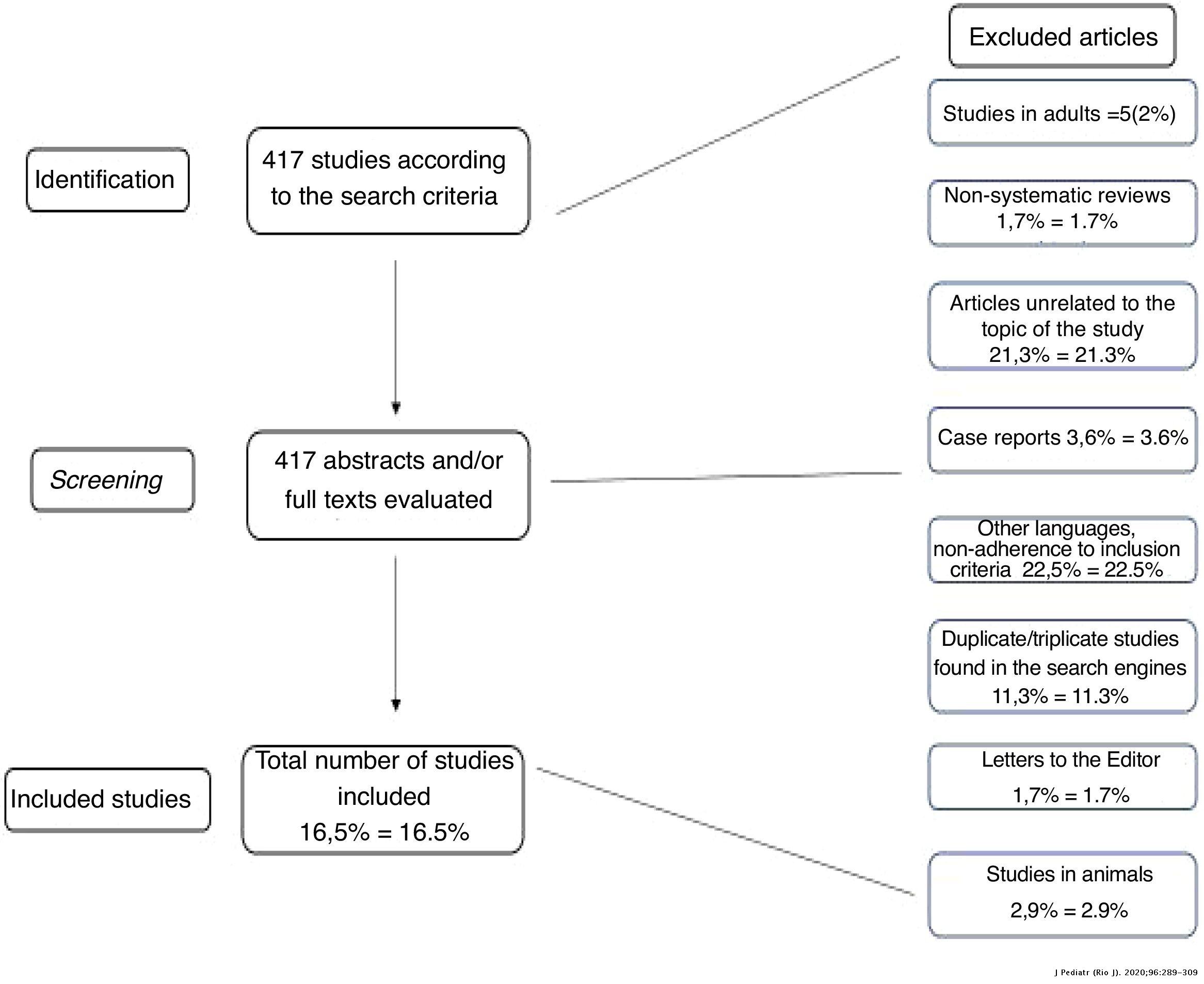
Cerebrospinal fluid lactate level as a diagnostic biomarker for bacterial meningitis in children, International Journal of Emergency Medicine
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) lactate is a potential biomarker for bacterial meningitis in children. To this end, we performed a single-center retrospective cohort study of children from Sao Paulo, Brazil, with CSF pleocytosis to evaluate the ability of CSF lactate to distinguish between children with bacterial and aseptic meningitis. We determined the optimum cutoff point for CSF lactate using receiver-operator curve (ROC) analysis. We identified 451 children of whom 40 (9%) had bacterial meningitis. Children with bacterial meningitis had a higher median CSF lactate level [9.6 mmol/l, interquartile range (IQR) 3.2-38.5 mmol/l bacterial meningitis vs. 2.0 mmol/l, IQR 1.2-2.8 mmol/l aseptic meningitis]. A CSF lactate cutoff point of 3.0 mmol/l had a sensitivity of 95% [95% confidence interval (CI) 83-99%), specificity of 94% (95% CI 90-96%) and negative predictive value of 99.3% (95% CI 97.7-99.9%) for bacterial meningitis. In combination with a validated meningitis clinical prediction rule, the CSF lactate level can be used to distinguish between bacterial and aseptic meningitis in children with CSF pleocytosis.

Biomedicines, Free Full-Text

Comparison between cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for differential diagnosis of acute meningitis

The cerebrospinal fluid neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is a sensitive biomarker for bacterial meningitis in children

PDF) CSF Lactate -An Independent and Reliable Biomarker among the CSF Parameters to Differentiate Bacterial Meningitis from Aseptic Meningitis
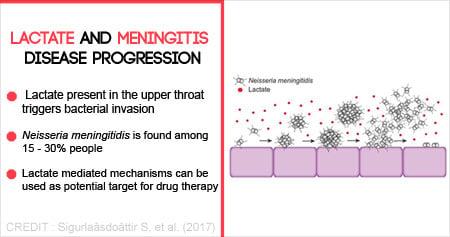
Lactate Triggers Invasion of Meningitis-Causing Bacteria into Blood
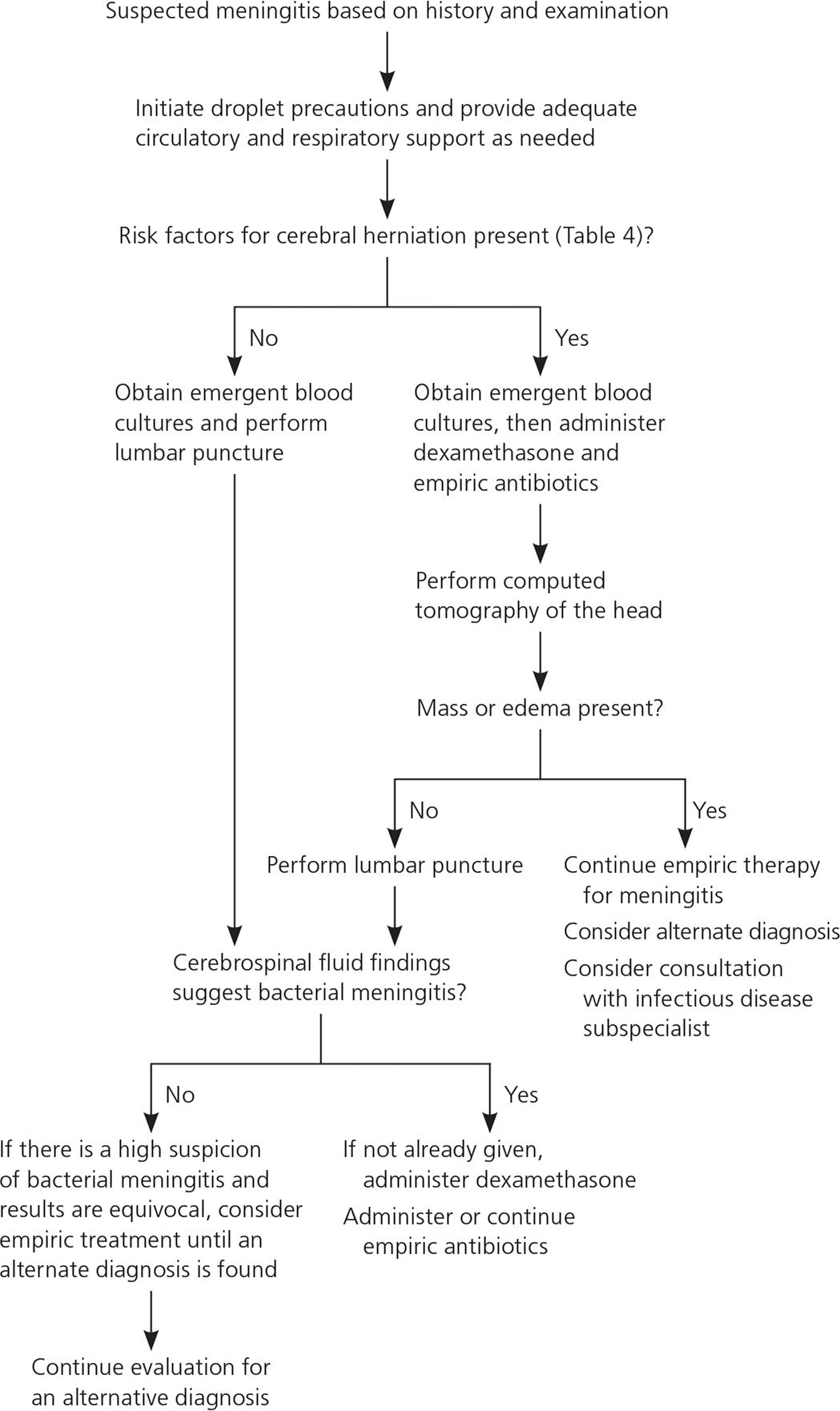
Aseptic and Bacterial Meningitis: Evaluation, Treatment, and Prevention
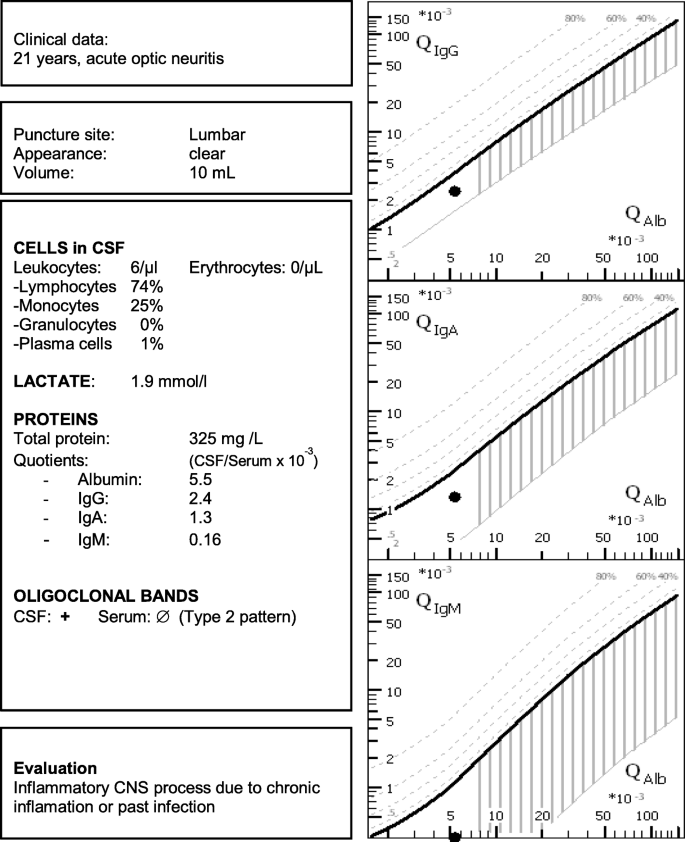
S1 guidelines “lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid analysis” (abridged and translated version), Neurological Research and Practice

PDF) Predictive Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid Lactate Level for the Diagnosis of Bacterial Meningitis following Cranial Surgery
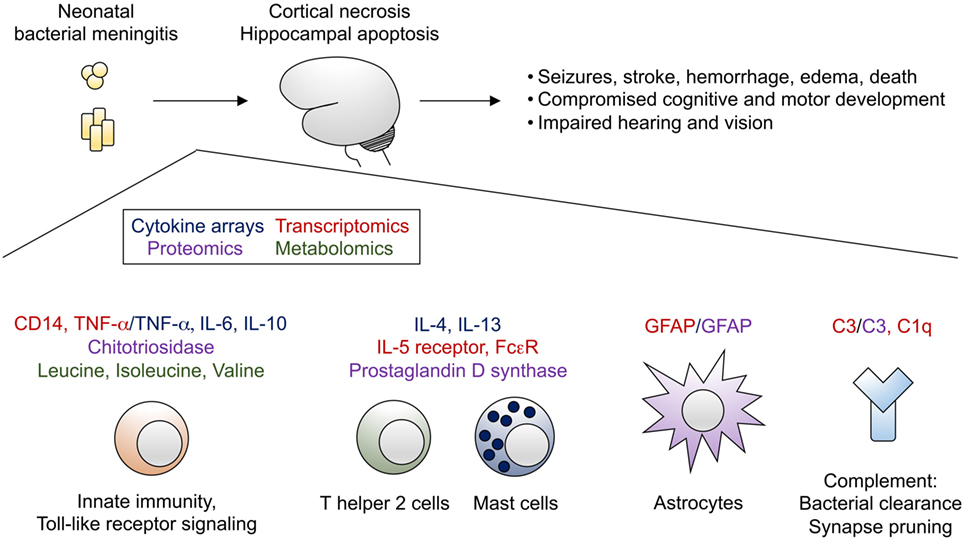
Frontiers Neonatal Meningitis: Overcoming Challenges in Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment with Omics
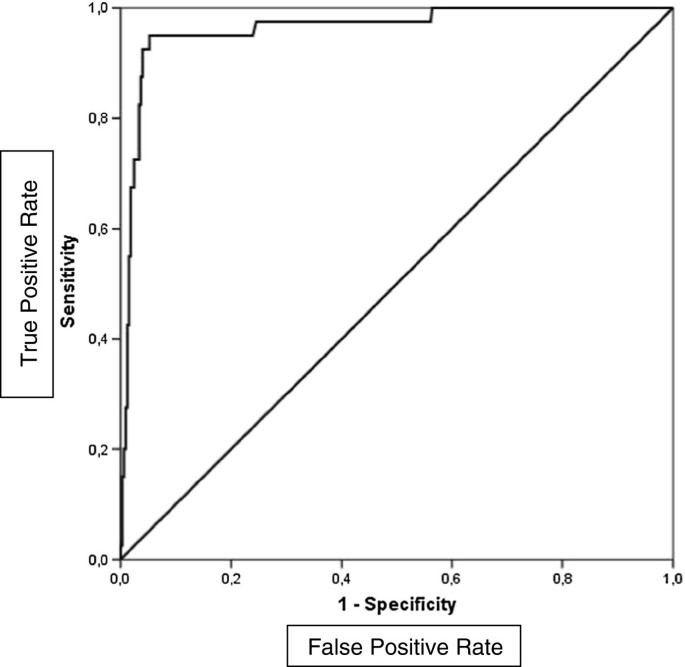
Cerebrospinal fluid lactate level as a diagnostic biomarker for bacterial meningitis in children, International Journal of Emergency Medicine

Interleukin-6 in cerebrospinal fluid as a biomarker of acute meningitis - Pablo García-Hernández, Belén Prieto, Eduardo Martínez-Morillo, Verónica Rodríguez, Francisco V Álvarez, 2016
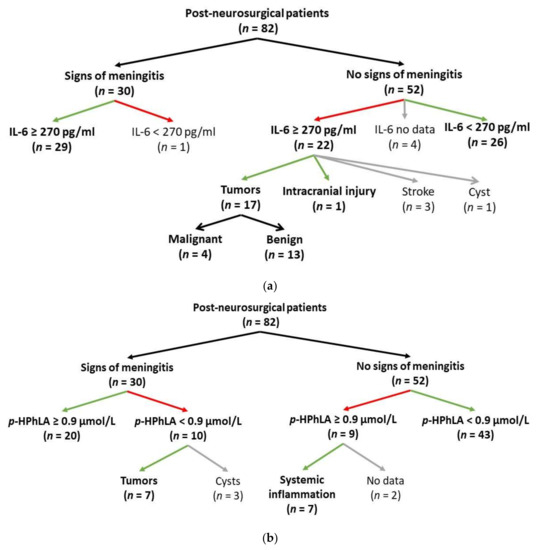
JPM, Free Full-Text

PDF) Role of cerebro spinal fluid lactate as a diagnostic marker for differentiation from bacterial and aseptic meningitis
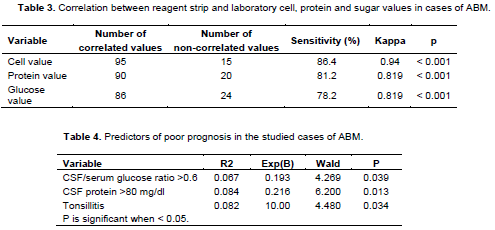
African Journal of Microbiology Research - etiological and predictive factors of acute meningitis in mansoura fever hospital, egypt
Cells, Free Full-Text
:strip_icc()/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_bc8228b6673f488aa253bbcb03c80ec5/internal_photos/bs/2022/R/i/gjQAX8SBiXCncdMIAYgw/mkhitaryan.jpeg)