Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Identifying tissue-specific molecular signatures of active regulatory elements is critical to understanding gene regulatory mechanisms. In this study, transcription start sites (TSS) and enhancers were identified using Cap analysis of gene expression (CAGE) across endometrial stromal cell (ESC) samples obtained from women with (n = 4) and without endometriosis (n = 4). ESC TSSs and enhancers were compared to those reported in other tissue and cell types in FANTOM5 and were integrated with RNA-seq and ATAC-seq data from the same samples for regulatory activity and network analyses. CAGE tag count differences between women with and without endometriosis were statistically tested and tags within close proximity to genetic variants associated with endometriosis risk were identified. Over 90% of tag clusters mapping to promoters were observed in cells and tissues in FANTOM5. However, some potential cell-type-specific promoters and enhancers were also observed. Regions of open chromatin identified using ATAC-seq provided further evidence of the active transcriptional regions identified by CAGE. Despite the small sample number, there was evidence of differences associated with endometriosis at 210 consensus clusters, including IGFBP5, CALD1 and OXTR. ESC TSSs were also located within loci associated with endometriosis risk from genome-wide association studies. This study provides novel evidence of transcriptional differences in endometrial stromal cells associated with endometriosis and provides a valuable cell-type specific resource of active TSSs and enhancers in endometrial stromal cells.
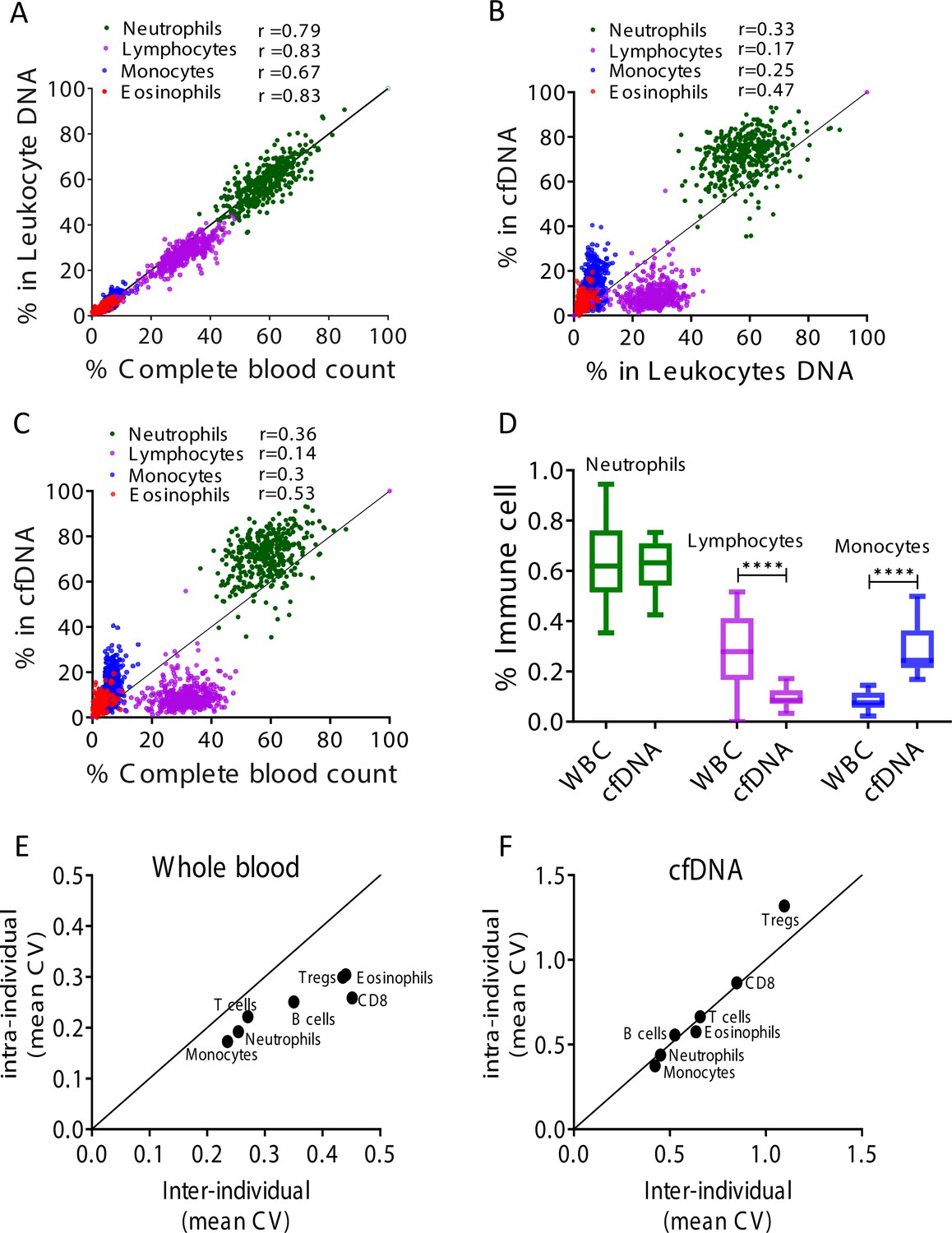
Remote immune processes revealed by immune-derived circulating cell-free DNA
Iec/Ts 62886 Get File - Colaboratory

Cell-Free Translation Systems
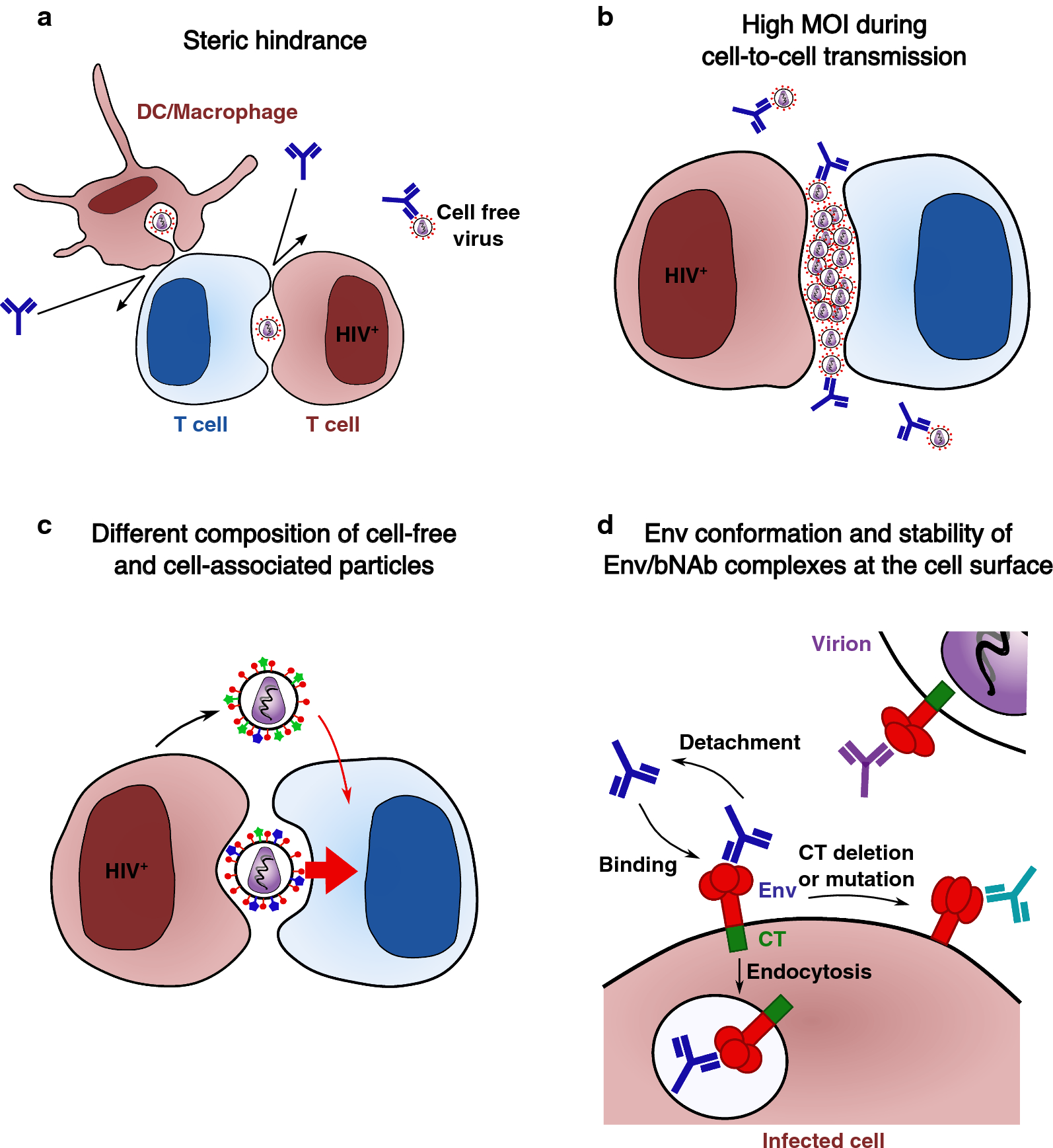
HIV-1 cell-to-cell transmission and broadly neutralizing antibodies, Retrovirology
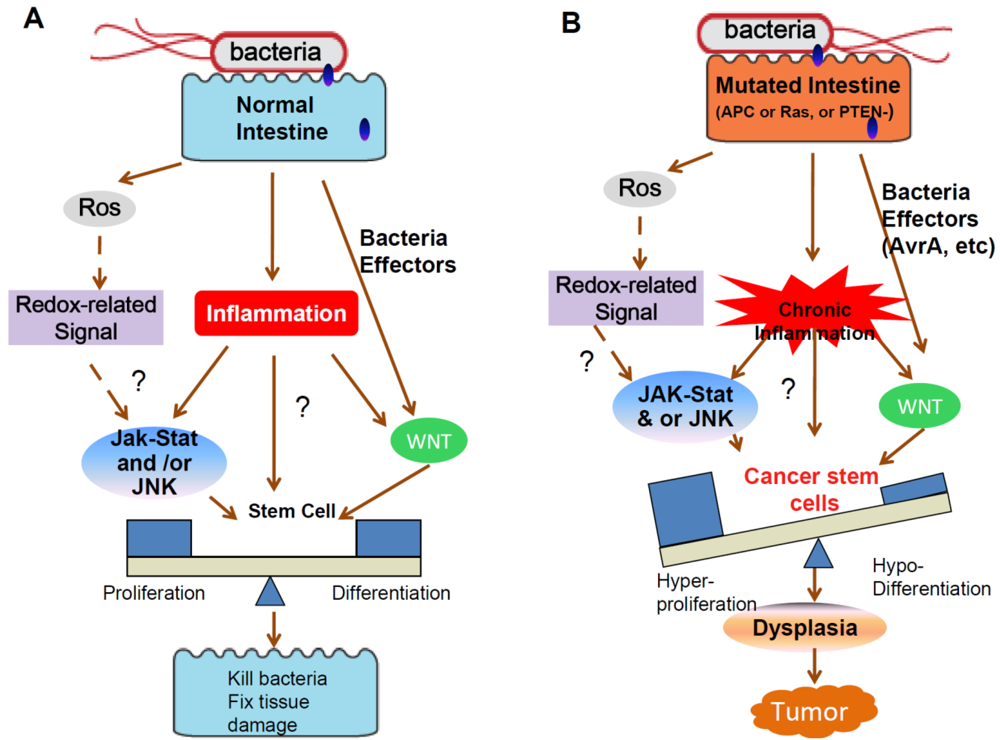
Cancers, Free Full-Text

Cells, Free Full-Text
An illustration of the full-duplex cell-free massive MIMO system.

Cell Circuits and Complex Tissues
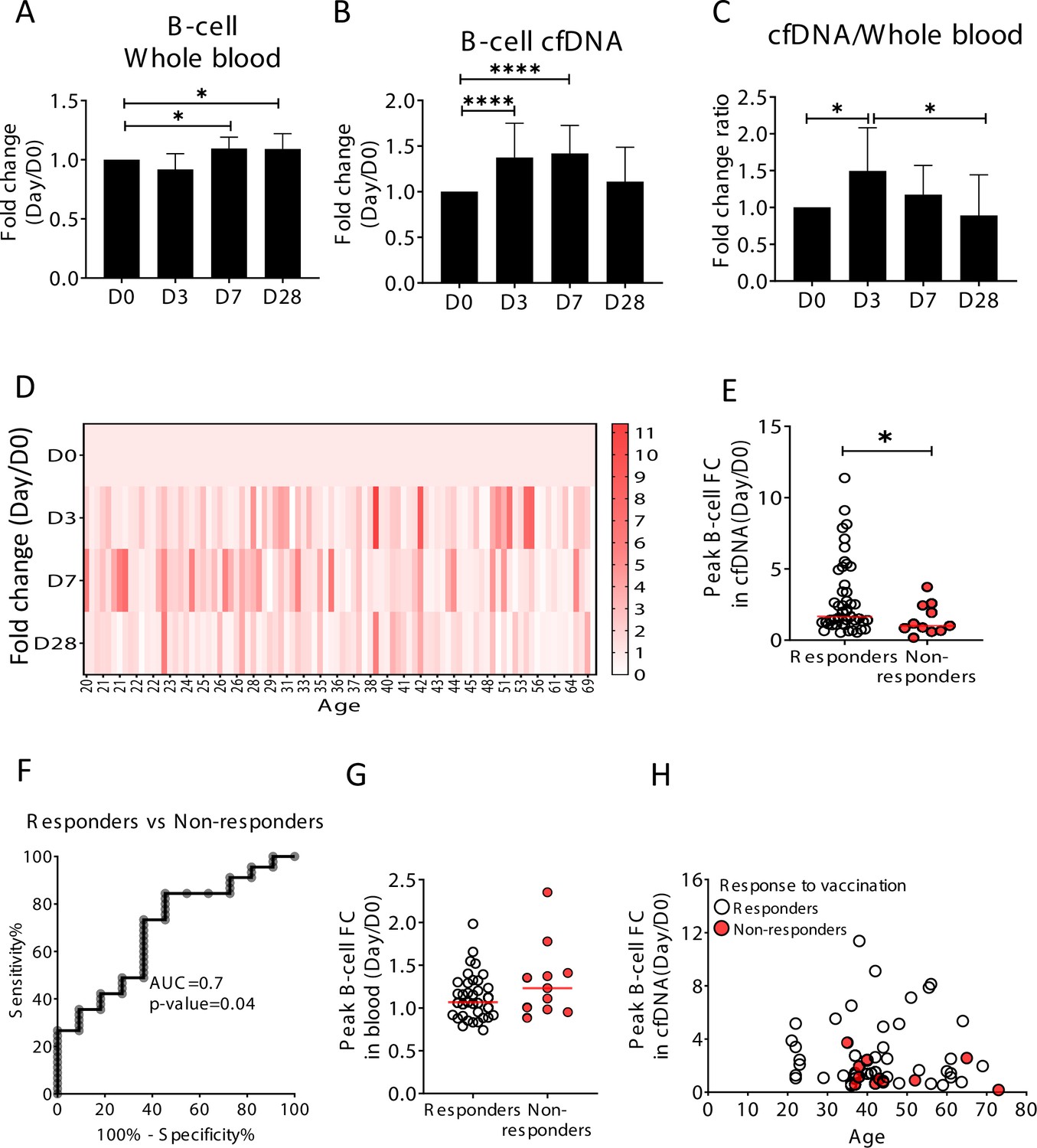
Remote immune processes revealed by immune-derived circulating cell-free DNA
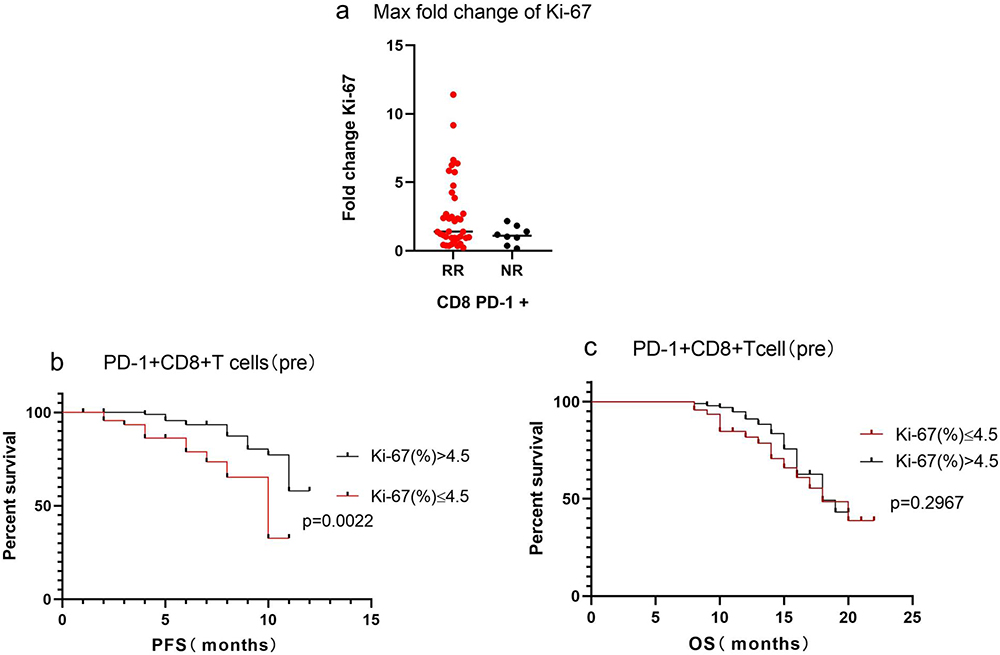
Cells, Free Full-Text

Cell-Free Synthetic Biology for Pathway Prototyping - ScienceDirect

Scheme of cell free cloning using DMF. ( A ) The full length construct
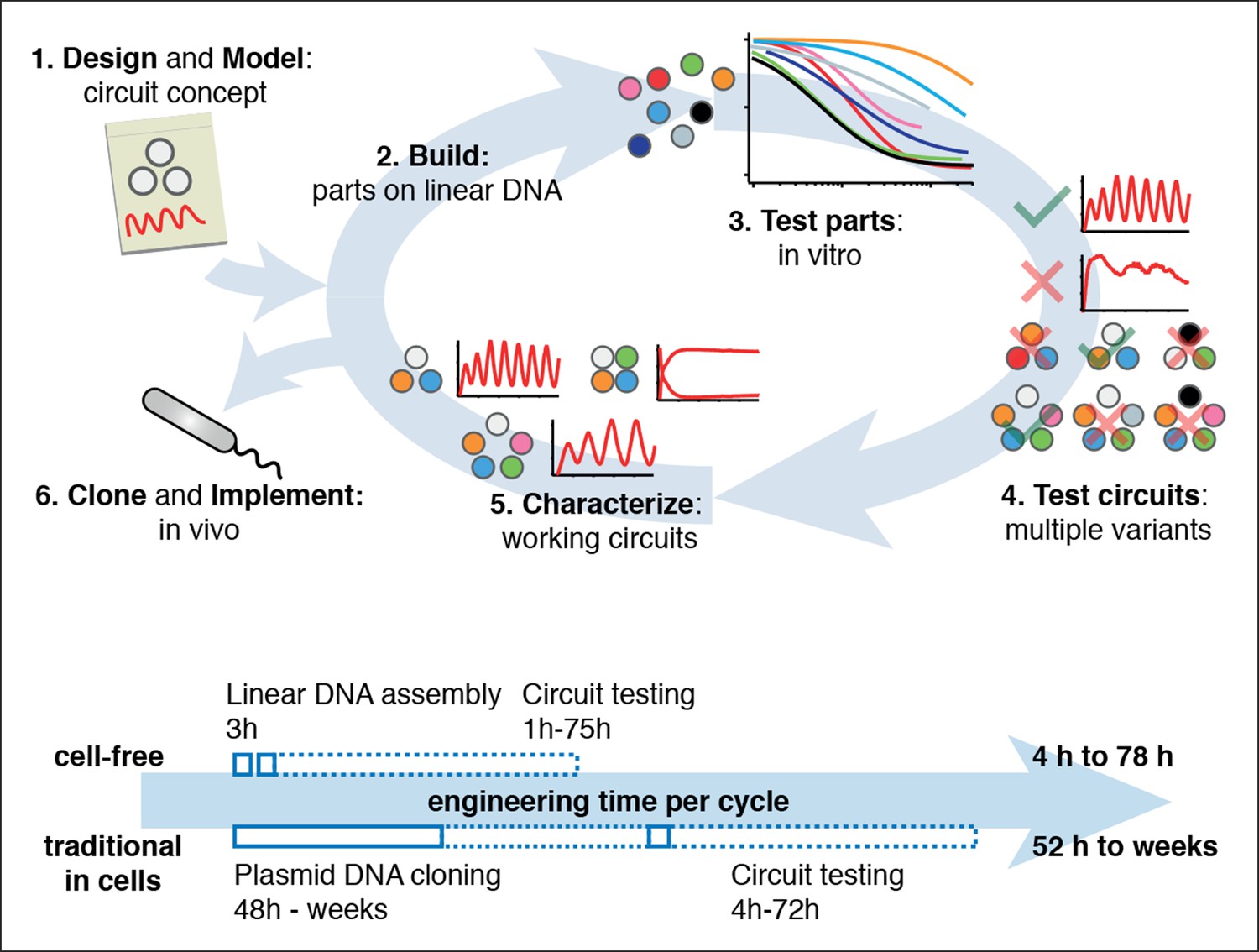
Rapid cell-free forward engineering of novel genetic ring oscillators
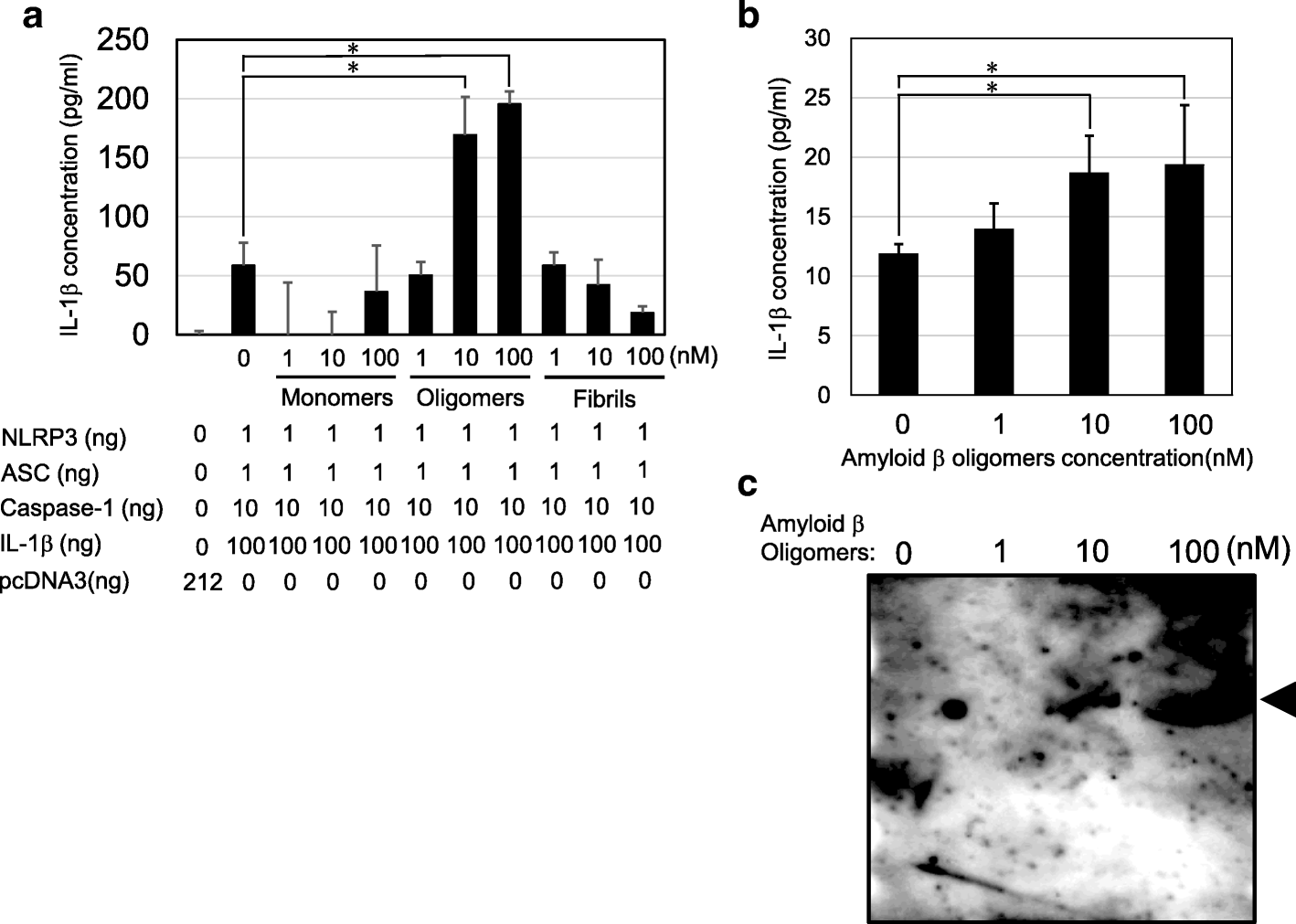
Amyloid β directly interacts with NLRP3 to initiate inflammasome activation: identification of an intrinsic NLRP3 ligand in a cell-free system, Inflammation and Regeneration
IAPP/amylin-induced interaction between NLRP3 and ASC in a cell-free