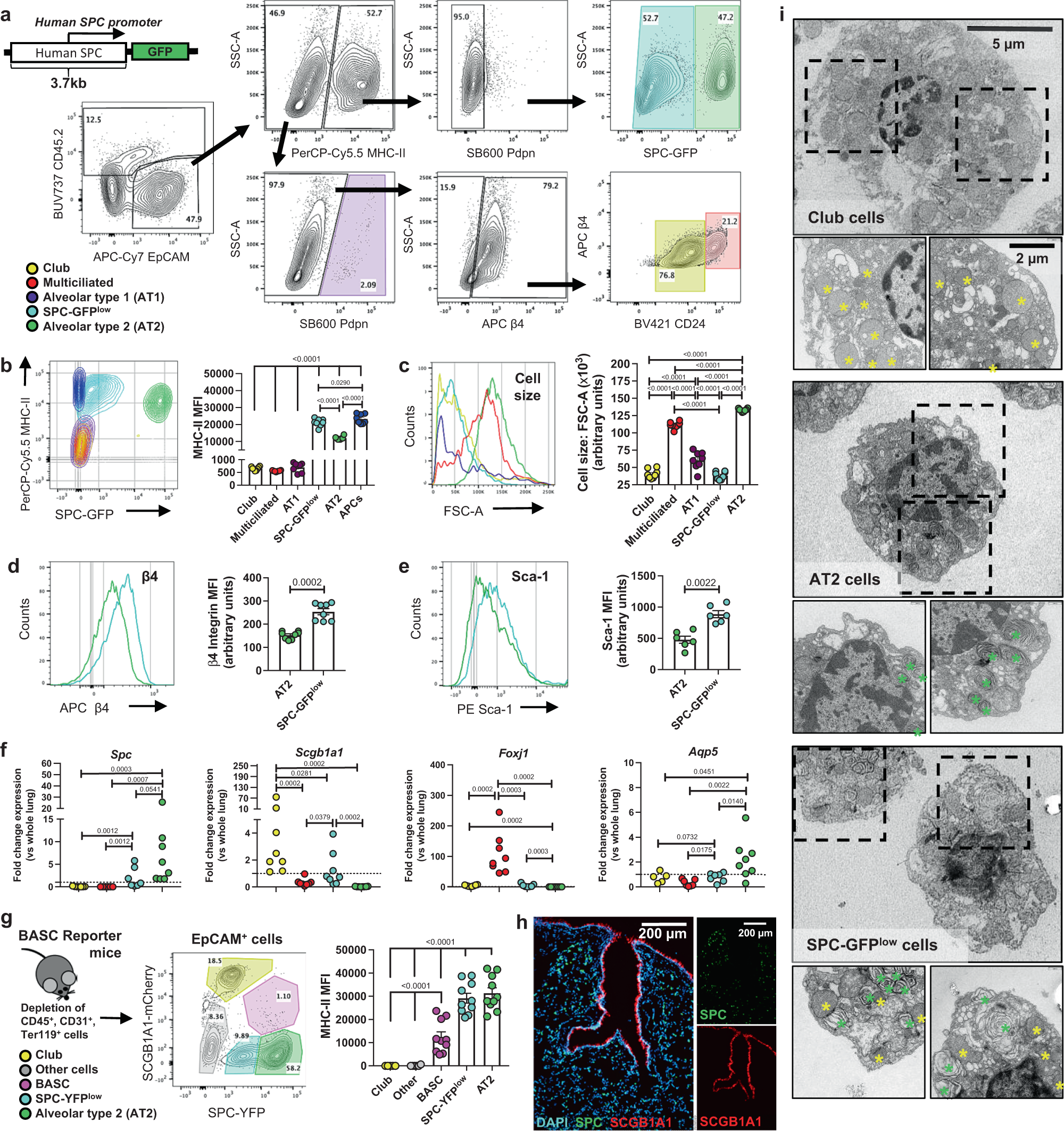
Cancers, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
The field of cancer research is famous for its incremental steps in improving therapy. The consistent but slow rate of improvement is greatly due to its meticulous use of consistent cancer biology models. However, as we enter an era of increasingly personalized cancer care, including chemo and radiotherapy, our cancer models must be equally able to be applied to all individuals. Patient-derived organoid (PDO) and organ-in-chip (OIC) models based on the micro-physiological bioengineered platform have already been considered key components for preclinical and translational studies. Accounting for patient variability is one of the greatest challenges in the crossover from preclinical development to clinical trials and patient derived organoids may offer a steppingstone between the two. In this review, we highlight how incorporating PDO’s and OIC’s into the development of cancer therapy promises to increase the efficiency of our therapeutics.

Blood Test for Cancer Screening
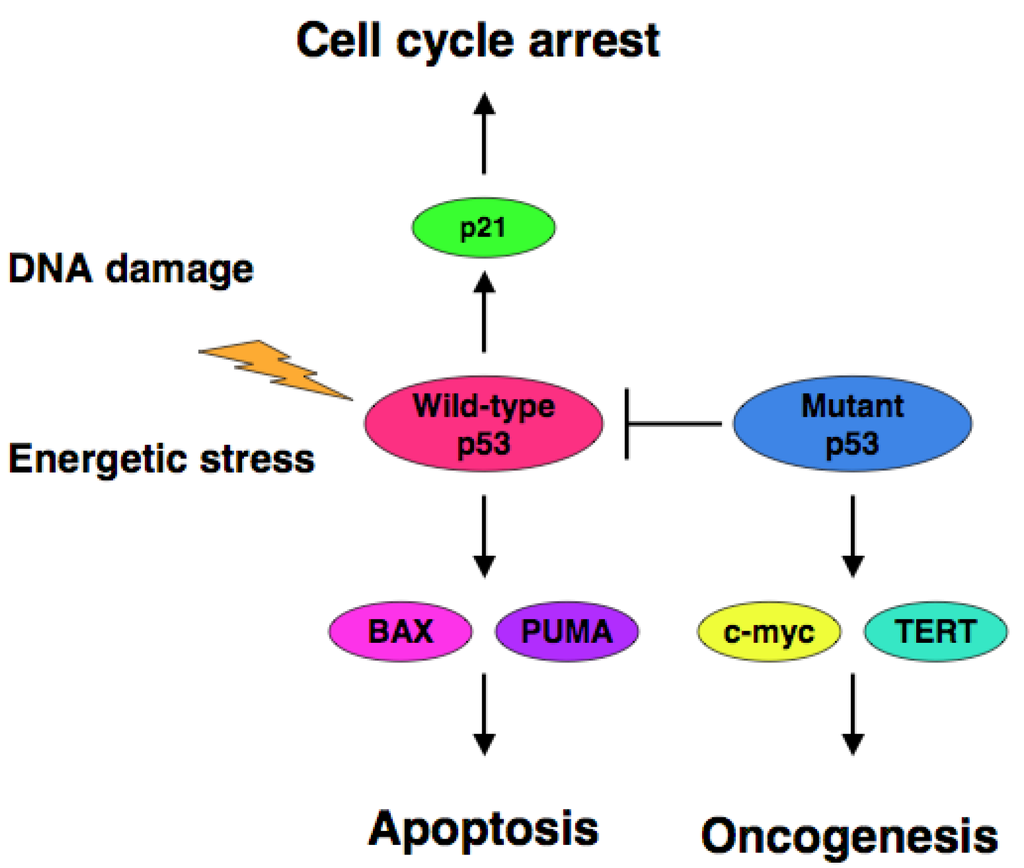
Cancers, Free Full-Text
Cancer Awareness Word Search – Free Printable

Cancer-Free, Third Edition by Bill Henderson - Audiobook

Cancer
CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians - Wiley Online Library

Pathology Outlines - Carcinoma-general

Trastuzumab after Adjuvant Chemotherapy in HER2-Positive Breast

Pembrolizumab for Persistent, Recurrent, or Metastatic Cervical

Mortality from leading cancers in districts of England from 2002

Cancer Horoscopes: Daily & Today

Pancreatic Cancer Action Network – Research, Patient Support

Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and