CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN Act as Receptors for SARS-CoV-2
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
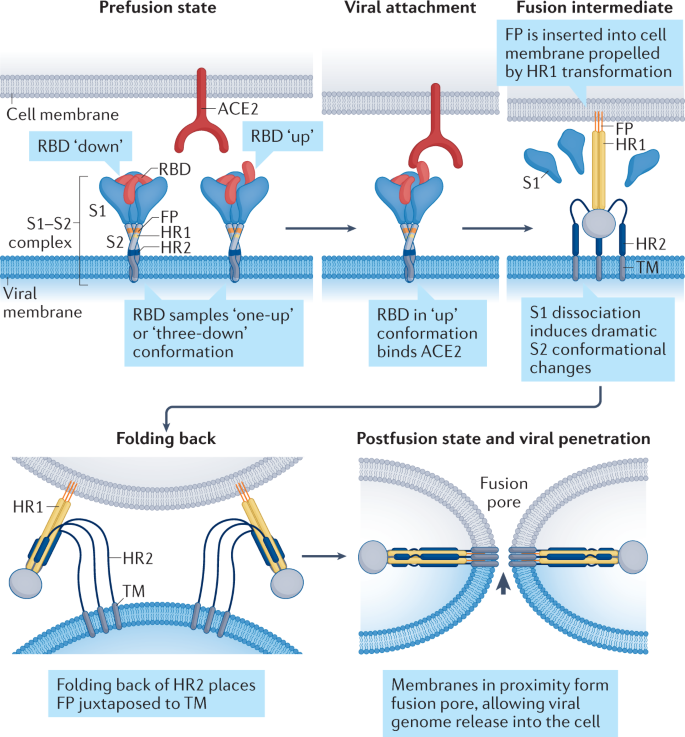
Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells
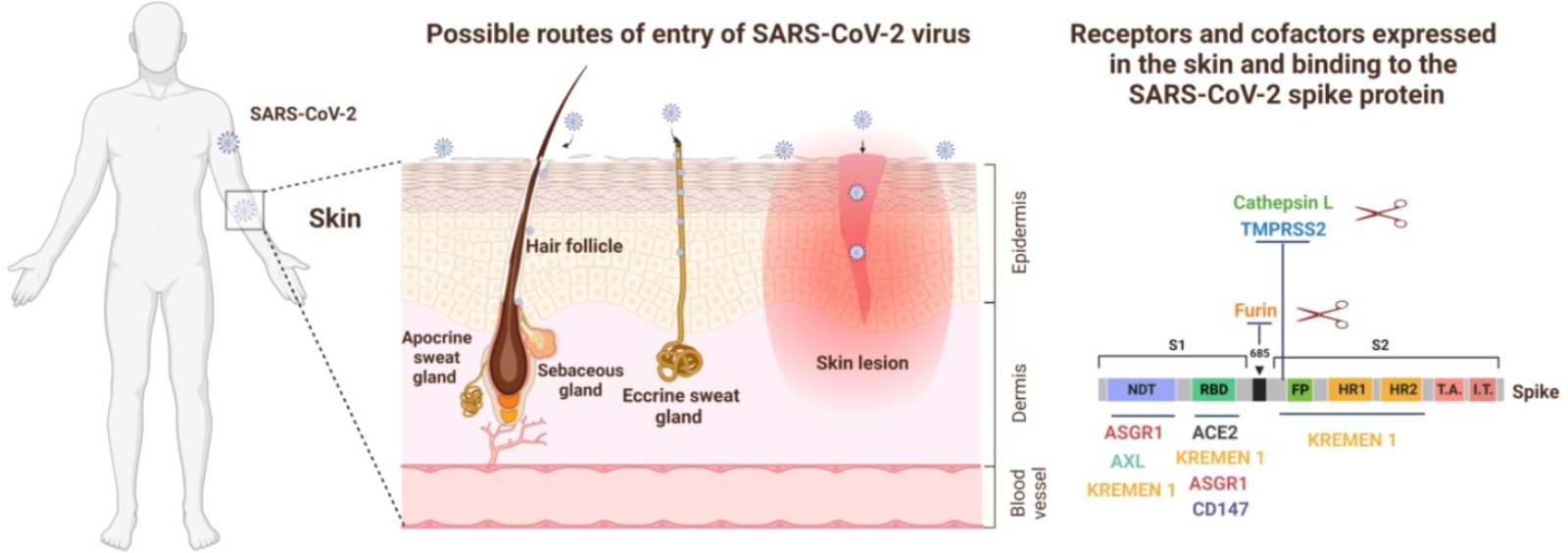
IJMS, Free Full-Text
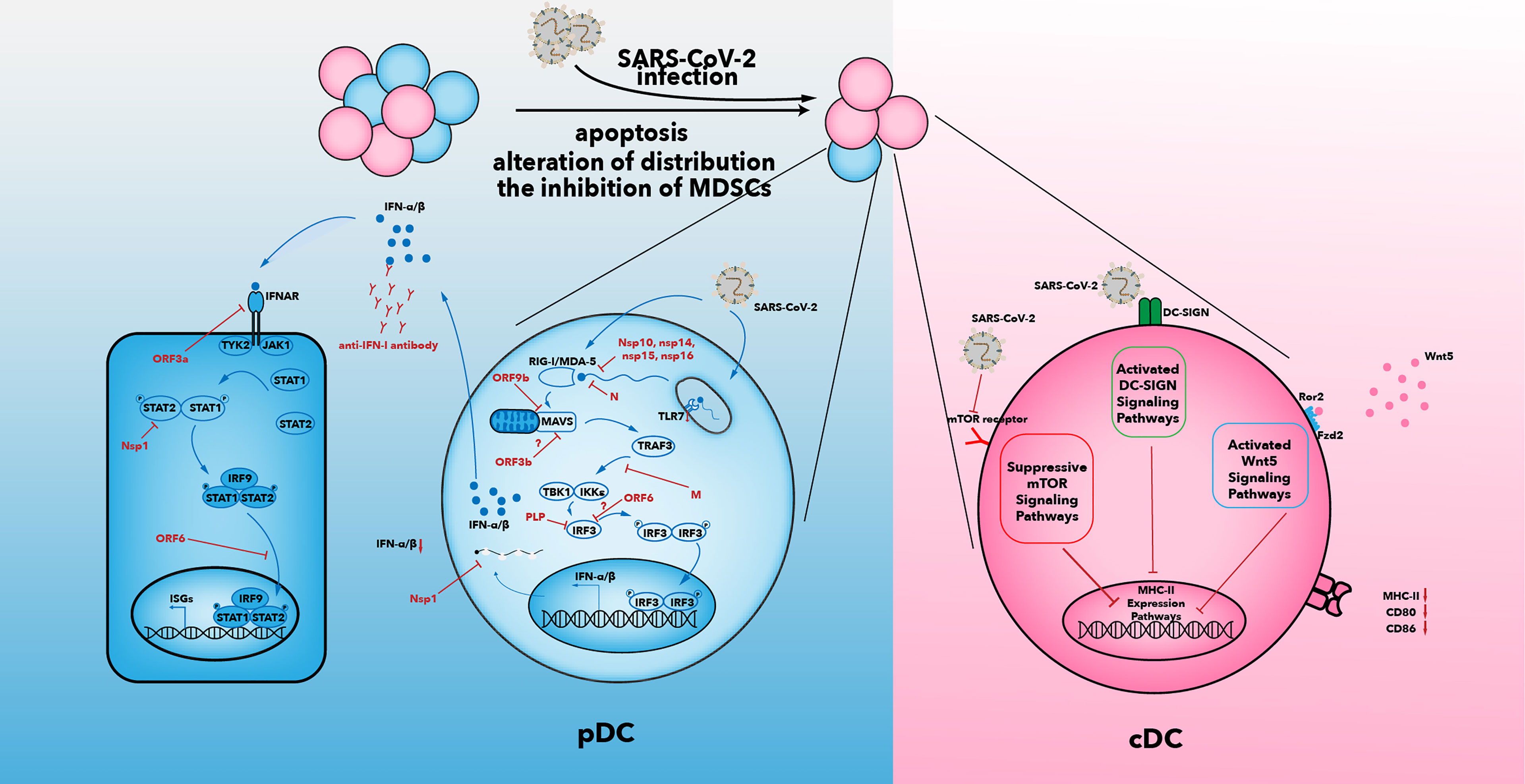
Frontiers Depletion and Dysfunction of Dendritic Cells: Understanding SARS -CoV-2 Infection

Role of DC-SIGN and L-SIGN receptors in HIV-1 vertical transmission - ScienceDirect
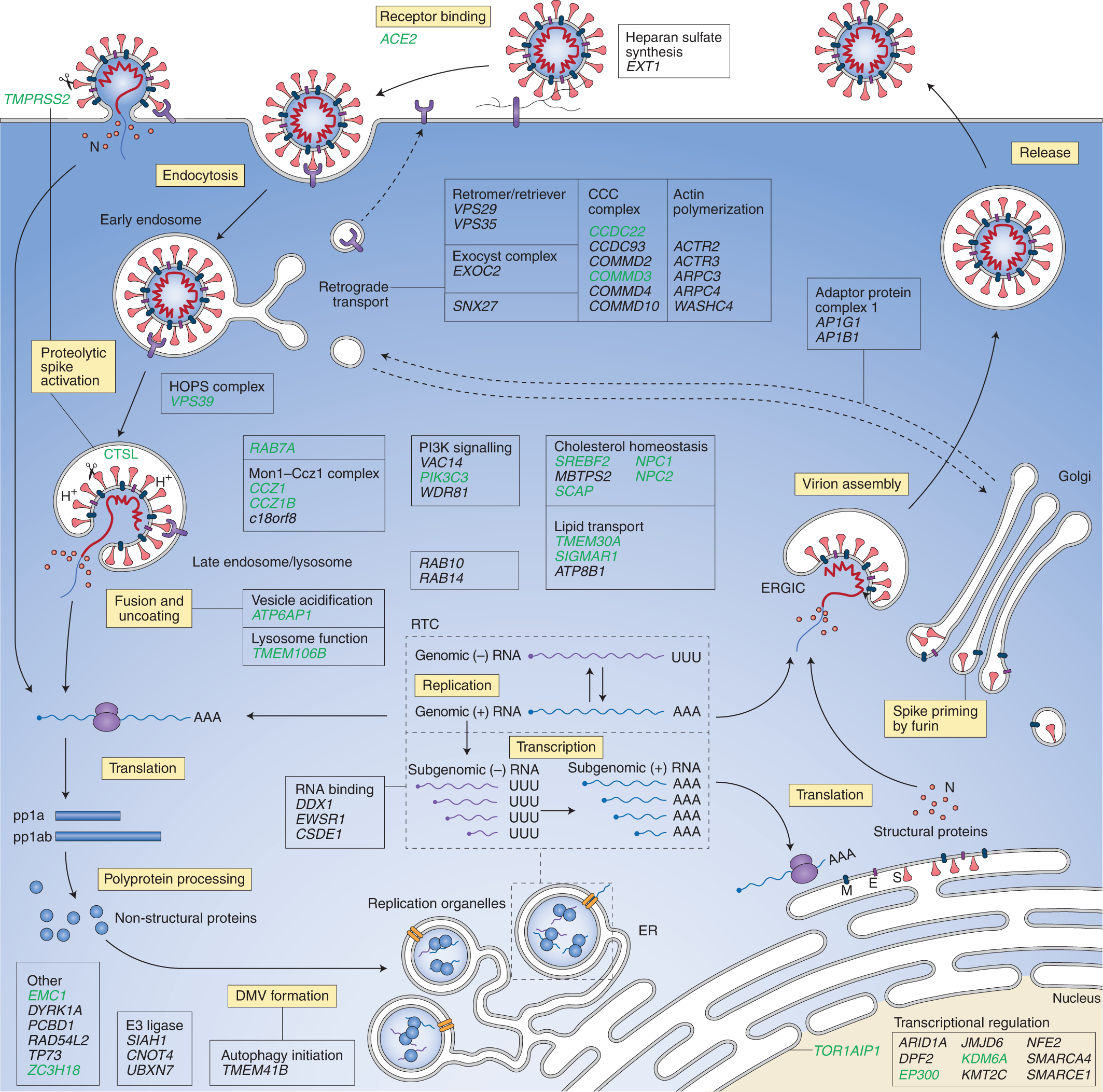
Cellular host factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection

DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR Interact with the Glycoprotein of Marburg Virus and the S Protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus

Full article: Immunouniverse of SARS-CoV-2

CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN Act as Receptors for SARS-CoV-2
Frontiers The role of DC-SIGN as a trans-receptor in infection by MERS-CoV

JCI Insight - L-SIGN is a receptor on liver sinusoidal endothelial cells for SARS-CoV-2 virus
Human Cell Receptors and Downstream Cascades: A Review of Molecular Aspects and Potential Therapeutic Targets in COVID-19, Archives of Pediatric Infectious Diseases

Host genetic factors determining COVID-19 susceptibility and severity - eBioMedicine

Comprehensive analysis of SARS‐CoV‐2 receptor proteins in human respiratory tissues identifies alveolar macrophages as potential virus entry site - Bräutigam - 2023 - Histopathology - Wiley Online Library

CD209L (L-SIGN) is a receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus

SARS-CoV-2 exacerbates proinflammatory responses in myeloid cells through C-type lectin receptors and Tweety family member 2 - ScienceDirect